Investigating and Optimizing Insulin Partitioning with Conjugated Au Nanoparticles in Aqueous Two-Phase Systems Using Response Surface Methodology
- PMID: 38434876
- PMCID: PMC10905728
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.3c09664
Investigating and Optimizing Insulin Partitioning with Conjugated Au Nanoparticles in Aqueous Two-Phase Systems Using Response Surface Methodology
Abstract
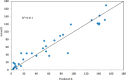
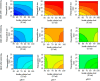
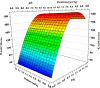
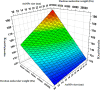
This study investigated the impact of bioconjugation on the partitioning of insulin, a clinically valuable protein, in an aqueous two-phase system. Gold nanoparticles of different sizes were synthesized and conjugated with insulin. Analysis of the conjugated insulin showed that the insulin remains fully active. Conjugated gold nanoparticles (AuNPs/insulin) were used in polyethylene glycol (PEG)-dextran aqueous two-phase systems to investigate the effect of pH, PEG and dextran molecular weights, PEG and dextran concentrations, AuNPs/insulin dosage, and nanoparticle size on the partition coefficient. These systems were chosen for their biocompatibility and low toxicity. Response surface methodology with D-optimal design was used to model and optimize these systems and their affected parameters. At the optimum condition of a pH = 8 system containing 21% PEG 4000, 5% dextran 100,000, and 100 IU AuNPs/insulin, the partition coefficient of AuNPs/insulin was found to be 192.96, which is in agreement with the empirical partition coefficient of 189.2. This is significantly higher than the partition coefficient of free insulin in a similar system. This approach could be used to overcome limitations in the feasibility of aqueous two-phase systems for industrial-scale purification of biomolecules and biopharmaceuticals.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


References
-
- Singla M.; Sit N. Theoretical Aspects and Applications of Aqueous Two-Phase Systems. ChemBioEng Rev. 2023, 10 (1), 65–80. 10.1002/cben.202200026. - DOI
-
- Mo Y. L.; Fischlschweiger M.; Zeiner T. Polymeric Aqueous Two Phase System with an Immobilized Phase by Cross-Linking. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61 (41), 15381–15389. 10.1021/acs.iecr.2c02204. - DOI
-
- Hatti-Kaul R.Aqueous two-phase systems. In Aqueous Two-Phase Systems: Methods and Protocols; Hatti-Kaul R., Ed.; Humana Totowa: NJ, 2008; Vol. 11, pp 1–10.
-
- Rahimpour F.; Hatti-Kaul R.; Mamo G. Response surface methodology and artificial neural network modelling of an aqueous two-phase system for purification of a recombinant alkaline active xylanase. Process Biochem. 2016, 51 (3), 452–462. 10.1016/j.procbio.2015.12.018. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
