Plk3 Enhances Cisplatin Sensitivity of Nonsmall-Cell Lung Cancer Cells through Inhibition of the PI3K/AKT Pathway via Stabilizing PTEN
- PMID: 38434880
- PMCID: PMC10905570
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.3c07271
Plk3 Enhances Cisplatin Sensitivity of Nonsmall-Cell Lung Cancer Cells through Inhibition of the PI3K/AKT Pathway via Stabilizing PTEN
Abstract
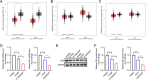
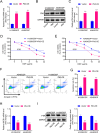
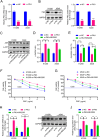
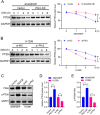
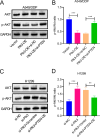
Polo-like kinase 3 (Plk3) is involved in tumor development with a tumor suppressive function. However, the effect of Plk3 on the chemoresistance remains unclear. It has been documented that activation of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway by PTEN loss significantly enhances chemoresistance in nonsmall-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). This study aims to evaluate the PTEN regulation by Plk3 and identify targets and underlying mechanisms that could be used to relieve chemoresistance. Our results showed that silencing Plk3 reduced PTEN expression and activated PI3K/AKT signaling by dephosphorylating and destabilizing PTEN in NSCLC cells. Reducing Plk3 expression promoted drug resistance to cisplatin (DDP), while overexpressing Plk3 promoted DDP sensitivity. However, these effects were attenuated when MK2206, a PI3K/AKT inhibitor, was applied. In conclusion, upregulation of Plk3 sensitized NSCLC cells toward DDP, which provides a potential target to restore DDP chemoresponse. We provided novel evidence that the PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway could be regulated by Plk3 through phosphorylation of PTEN and highlighted the critical role of Plk3 in the DDP resistance of NSCLC.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
