Streamlined Water-Leaching Preconcentration Method As a Novel Analytical Approach and Its Coupling to Dispersive Micro-Solid-Phase Extraction Based on Synthetically Modified (Fe/Co) Bimetallic MOFs
- PMID: 38434905
- PMCID: PMC10905590
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.3c08218
Streamlined Water-Leaching Preconcentration Method As a Novel Analytical Approach and Its Coupling to Dispersive Micro-Solid-Phase Extraction Based on Synthetically Modified (Fe/Co) Bimetallic MOFs
Abstract
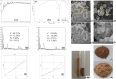
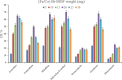
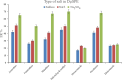
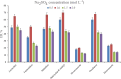
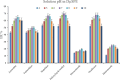
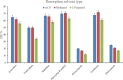
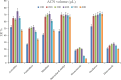
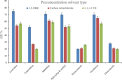
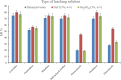
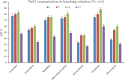
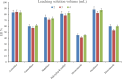
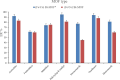
The streamlined water-leaching preconcentration method is introduced as a novel preconcentration method in this study. The approach has many benefits including low consumption of organic solvent and deionized water and operation time, energy-saving, no need for dispersion or evaporation, and implementation of more efficient preconcentration. Also, a methodological study was done on the synthesis of (Fe/Co) bimetallic-organic framework that eased the synthesis procedure, decreased its time, and enhanced its analytical performance by increasing its surface area, total pore volume, and average pore diameter parameters. To perform the extraction, bi-MOF particles were added into the solution of interest enriched with sodium sulfate. After vortexing to adsorb the analytes, centrifugation isolated the sorbent particles. A microliter-volume of acetonitrile and 1,2-dibromoethane mixture was used for desorption aim via vortexing. After the separation of the organic phase and transferring it into a conical bottom glass test tube, a milliliter volume of sodium chloride solution was applied to leach the organic phase. A gas chromatograph equipped with a flame ionization detector was applied for the injection of the extracted phase. The method was applied for the extraction and preconcentration of some pesticides from juice samples. Wide linear ranges (5.44-1600 μg L-1), low relative standard deviations (3.1-4.5% for intra- (n = 6) and 3.5-5.2% for interday (n = 4) precisions), high extraction recoveries (61-95%), enrichment factors (305-475), and low limits of detection (0.67-1.65 μg L-1) and quantification (2.21-5.44 μg L-1) were obtained for the developed method.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An all-embracing analytical method comprising modified QuEChERS-dispersive micro-solid-phase extraction-dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction using FeGA MOF for the extraction and preconcentration of pesticides simultaneously from juice and flesh of watermelon.Anal Sci. 2023 Aug;39(8):1201-1214. doi: 10.1007/s44211-023-00330-8. Epub 2023 Apr 5. Anal Sci. 2023. PMID: 37017814
-
NiGA MOF-based dispersive micro solid phase extraction coupled to temperature-assisted evaporation using low boiling point solvents for the extraction and preconcentration of butylated hydroxytoluene and some phthalate and adipate esters.RSC Adv. 2023 Oct 17;13(43):30378-30390. doi: 10.1039/d3ra04612e. eCollection 2023 Oct 11. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 37854488 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of dispersive solid phase extraction and deep eutectic solvent-based air-assisted liquid-liquid microextraction followed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry as an efficient analytical method for the quantification of some tricyclic antidepressant drugs in biological fluids.J Chromatogr A. 2018 Oct 12;1571:84-93. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2018.08.022. Epub 2018 Aug 10. J Chromatogr A. 2018. PMID: 30119972
-
Pesticide content analysis of red and yellow watermelon juices through a solid phase microextraction using a green copper-based metal-organic framework synthesized in water followed by a liquid phase microextraction procedure.Anal Sci. 2023 Mar;39(3):357-368. doi: 10.1007/s44211-022-00249-6. Epub 2022 Dec 23. Anal Sci. 2023. PMID: 36562955
-
Extraction and preconcentration of parabens from the human follicular fluid through dispersive micro solid phase extraction using microporous MIL-68 (In) followed by in-situ effervescence-boosted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2024 Mar 15;240:115926. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2023.115926. Epub 2023 Dec 20. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2024. PMID: 38142500
References
-
- Nasiri M.; Ahmadzadeh H.; Amiri A. Sample preparation and extraction methods for pesticides in aquatic environments: A review. Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 123, 11577210.1016/j.trac.2019.115772. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
