A Case of Aggressive Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma With Aberrant Cytoplasmic p53 Aggregation
- PMID: 38434916
- PMCID: PMC10905281
- DOI: 10.21873/cdp.10309
A Case of Aggressive Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma With Aberrant Cytoplasmic p53 Aggregation
Abstract
Background: Immunohistochemistry for p53 was a well-established method for cancer diagnosis in pathology. Aberrant cytoplasmic p53 positivity reflects the accumulation of p53 aggregates, which has been shown to be associated with chemoresistance and to be a predictive marker of a worse clinical course in ovarian cancer.
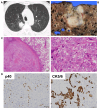
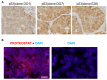
Case report: A 65-year-old Japanese man was diagnosed with lung cancer, and surgical resection was performed. Multiple metastasis were found 21 months post-surgery. The lesions were resistant to chemotherapy, and he succumbed to the disease 29 months post-surgery. The resected primary lesion was pathologically diagnosed as squamous cell carcinoma, with notable cytoplasmic p53 positivity indicated by immunohistochemistry.
Conclusion: Notable aberrant cytoplasmic accumulation of p53 aggregate was observed in the cancer cells of this case. Chemotherapy was ineffective for the recurrent lesions, suggesting a role of p53 aggregates in chemoresistance. Pathological analysis of p53 via immunohistochemistry may be useful in predicting chemoresistance of lung squamous cell carcinoma.
Keywords: Lung; aggressive; p53 aggregation; squamous cell carcinoma.
Copyright 2024, International Institute of Anticancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
All Authors have no conflicts of interest to declare in relation to this study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aberrant expression of p53 or the epidermal growth factor receptor is frequent in early bronchial neoplasia and coexpression precedes squamous cell carcinoma development.Cancer Res. 1995 Mar 15;55(6):1365-72. Cancer Res. 1995. PMID: 7882337
-
Cytoplasmic p53 aggregates accumulated in p53-mutated cancer correlate with poor prognosis.PNAS Nexus. 2022 Jul 25;1(3):pgac128. doi: 10.1093/pnasnexus/pgac128. eCollection 2022 Jul. PNAS Nexus. 2022. PMID: 36741442 Free PMC article.
-
Acantholytic squamous cell carcinoma of the lung with marked lymphogenous metastases and high titers of myeloperoxidase-antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies: a case report.BMC Cancer. 2018 Mar 16;18(1):300. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4218-8. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29548309 Free PMC article.
-
INGN 201: Ad-p53, Ad5CMV-p53, adenoviral p53, p53 gene therapy--introgen, RPR/INGN 201.Drugs R D. 2007;8(3):176-87. doi: 10.2165/00126839-200708030-00005. Drugs R D. 2007. PMID: 17472413 Review.
-
[Clinicopathological study on primary lung cancer--immunohistochemical expression of p53 suppressor gene and bcl-2 oncogene in relation to prognosis].Rinsho Byori. 1996 Jan;44(1):32-41. Rinsho Byori. 1996. PMID: 8691638 Review. Japanese.
References
-
- Forde PM, Spicer J, Lu S, Provencio M, Mitsudomi T, Awad MM, Felip E, Broderick SR, Brahmer JR, Swanson SJ, Kerr K, Wang C, Ciuleanu TE, Saylors GB, Tanaka F, Ito H, Chen KN, Liberman M, Vokes EE, Taube JM, Dorange C, Cai J, Fiore J, Jarkowski A, Balli D, Sausen M, Pandya D, Calvet CY, Girard N, CheckMate 816 Investigators Neoadjuvant nivolumab plus chemotherapy in resectable lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2022;386(21):1973–1985. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2202170. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
