Assessment the value of Pyroptosis-Associated Gasdermin family genes in hepatocellular carcinoma: A Multi-Omics Comprehensive Analysis
- PMID: 38434972
- PMCID: PMC10905399
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.88887
Assessment the value of Pyroptosis-Associated Gasdermin family genes in hepatocellular carcinoma: A Multi-Omics Comprehensive Analysis
Abstract
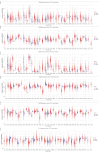
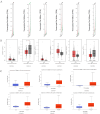
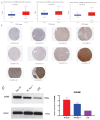
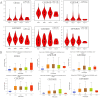
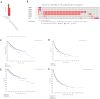
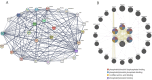
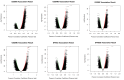
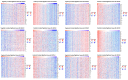
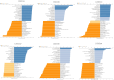
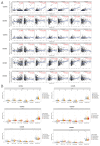
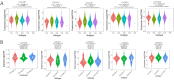
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the common primary cancers of the liver worldwide and leading cause of mortality. Gasdermins (GSDMs) family genes play an important role in the regulation of the normal physiological processes and have been implicated in multiple diseases. However, little is known about the relationship between different GSDMs proteins and HCC. The aim of this study was to explore the potential relationship between the expression, prognosis, genetic variation and immune infiltration of GSDMs family genes and HCC. Methods: We used different bioinformatics common public databases such as GSCA, GEPIA, UALCAN, HPA, Kaplan-Meier Plotter, LinkedOmics, GeneMANIA, STRING, cBioPortal, TIMER and TISIDB to analyze the differential expression of the different GSDMs, prognostic value, genetic alterations, immune cell infiltration and their functional networks in HCC patients. Results: All the members of the GSDMs family exhibited elevated mRNA expression levels in LIHC compared to the normal tissues, while only GSDMB, GSDMD and GSDME showed enhanced protein expression. The mRNA expression of most GSDMs members was found to be elevated in HCC patients at stages I-III (clinical stage) compared to the normal subjects. The expression of GSDMD was correlated with OS and DSS of patients, whereas GSDME was correlated with OS, DSS and RFS of patients. Gene amplification was observed to be main mode of variation in members of the GSDMs family. KEGG pathway analysis showed that genes associated with different members of the GSDMs family were enriched in the pathways of S. aureus infection, intestinal immunity, ribosome and protein assembly, oxidative phosphorylation, osteoclast differentiation and Fc gamma (γ) R-mediated phagocytosis. In addition, expression of both GSDMA and GSDME were found to be correlated most significantly with infiltration of immune cells, while GSDMA and GSDME somatic cell copy number alteration (CAN) were correlated significantly with the infiltration of immune cells. All GSDMs were noted to be associated with distinct subtypes of immune cells, except GSDMC. Conclusions: Our findings have provided useful insights to better understand the roles and functions of GSDMs in HCC that can provide novel direction for developing therapeutic modalities for HCC, including immunotherapy.
Keywords: Bioinformatics analysis; GSDME; GSDMs; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Prognosis; immune infiltration.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Integrated analysis of expression, prognostic value and immune infiltration of GSDMs in hepatocellular carcinoma.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Nov 3;13(21):24117-24135. doi: 10.18632/aging.203669. Epub 2021 Nov 3. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34731088 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic and prognostic value of the gasdermins in gastric cancer.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2024 Nov 25;57:e13817. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X2024e13817. eCollection 2024. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2024. PMID: 39607202 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value and immune infiltration of the gasdermin family in lung adenocarcinoma.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 25;12:1043862. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1043862. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36505798 Free PMC article.
-
The Pyroptotic and Nonpyroptotic Roles of Gasdermins in Modulating Cancer Progression and Their Perspectives on Cancer Therapeutics.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2023 May 31;71(1):14. doi: 10.1007/s00005-023-00678-9. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2023. PMID: 37258998 Review.
-
Gasdermins: pore-forming activities and beyond.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2020 May 26;52(5):467-474. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmaa016. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2020. PMID: 32294153 Review.
Cited by
-
GSDMD is associated with survival in human breast cancer but does not impact anti-tumor immunity in a mouse breast cancer model.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 19;15:1396777. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1396777. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39224600 Free PMC article.
-
Gasdermin D (GSDM D) as a Potential Diagnostic Biomarker in Bladder Cancer: New Perspectives in Detection.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Dec 18;16(24):4213. doi: 10.3390/cancers16244213. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39766111 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Villanueva A. Hepatocellular Carcinoma. The New England journal of medicine. 2019;380:1450–62. - PubMed
-
- Forner A, Reig M, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet (London, England) 2018;391:1301–14. - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM, Kelley RK, Villanueva A, Singal AG, Pikarsky E, Roayaie S. et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nature reviews Disease primers. 2021;7:6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

