Comparative Analysis of Diagnostic Efficacy in Primary Hyperparathyroidism: A Comparison Analysis of 11C-Choline PET/CT, Neck Ultrasonography, 99mTc-MIBI Dual-Phase Planar Scintigraphy, and 99mTc-MIBI SPECT/CT Imaging
- PMID: 38434973
- PMCID: PMC10905405
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.91483
Comparative Analysis of Diagnostic Efficacy in Primary Hyperparathyroidism: A Comparison Analysis of 11C-Choline PET/CT, Neck Ultrasonography, 99mTc-MIBI Dual-Phase Planar Scintigraphy, and 99mTc-MIBI SPECT/CT Imaging
Abstract
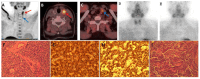
Objective: To compare the diagnostic efficacy of 11C-choline PET/CT, neck ultrasonography, 99mTc-MIBI dual-phase planar scintigraphy, and 99mTc-MIBI SPECT/CT imaging in the diagnosis of primary hyperparathyroidism (PHPT). Methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis of 32 patients with PHPT who visited the Nuclear Medicine Department of Jilin University China-Japan Union Hospital between January 2019 and December 2022. All patients underwent 11C-choline PET/CT, neck ultrasonography, 99mTc-MIBI dual-phase planar scintigraphy, and 99mTc-MIBI SPECT/CT examinations within two months before surgery. Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value of each imaging study were compared using postoperative pathology and follow-up results. Diagnostic efficacy was further analyzed using ROC curve analysis. Factors influencing on 99mTc-MIBI imaging were also investigated. Results: A total of 35 lesions were resected in the 32 patients. The diagnostic sensitivity of 11C-choline PET/CT, neck ultrasonography, 99mTc-MIBI dual-phase planar scintigraphy, and 99mTc-MIBI SPECT/CT was 88.2%, 52.9%, 58.8%, and 67.6%, respectively. Specificity was 96.8%, 95.7%, 96.8%, and 95.7%, respectively. Positive predictive values were 90.9%, 81.8%, 86.9%, and 85.2%, respectively, and negative predictive values were 95.7%, 84.9%, 86.7%, and 89.1%, respectively. The areas under the ROC curve (AUC) were 0.925, 0.743, 0.778, and 0.817, respectively. Among them, 11C-choline PET/CT had higher sensitivity and AUC than other imaging studies (p<0.05), while specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value were similar (p>0.05). The positive group in 99mTc-MIBI SPECT/CT imaging had significantly larger lesion diameters than the negative group (P<0.05), while preoperative blood calcium and PTH showed no statistical differences (P>0.05). Conclusion: 11C-choline PET/CT demonstrates superior preoperative diagnostic efficacy for PHPT compared to neck ultrasonography, 99mTc-MIBI dual-phase planar scintigraphy, and 99mTc-MIBI SPECT/CT. Lesion size may be the primary factor affecting the sensitivity of 99mTc-MIBI imaging.
Keywords: 11C-choline; 99mTc-MIBI; PET; SPECT; neck ultrasonography; primary hyperparathyroidism.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

References
-
- Giovanella L, Bacigalupo L, Treglia G, Piccardo A. Will 18F-fluorocholine PET/CT replace other methods of preoperative parathyroid imaging? Endocrine. 2021;71:285–297. - PubMed
-
- Rao SD. Epidemiology of parathyroid disorders. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;32:773–780. - PubMed
-
- Vadhwana B, Currow C, Bowers D, Groot-Wassink T. Impact on Quality of Life After Parathyroidectomy for Asymptomatic Primary Hyperparathyroidism. J Surg Res. 2021;261:139–145. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

