MicroRNA-485-5p targets keratin17 to regulate pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and invasion via the FAK / SRC / ERK pathway
- PMID: 38434984
- PMCID: PMC10905395
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.90689
MicroRNA-485-5p targets keratin17 to regulate pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and invasion via the FAK / SRC / ERK pathway
Abstract
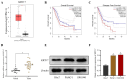
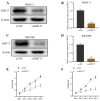
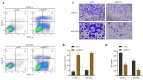
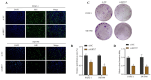
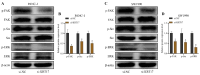
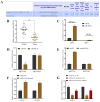
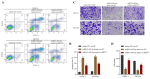
Background: It is crucial to probe into the biological effect and mechanism of miRNA-485-5p regulating keratin 17 (KRT17) in pancreatic cancer (PC) to understand its pathogenesis and identify potential biological targets. Methods: The bioinformatics means were used to evaluate the clinical significance of KRT17 expression in the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. TargetScan database analysis in conjunction with dual luciferase and RNA Immunoprecipitation (RIP) experiments was used to probe the interaction relationship of miRNA-485-5p with KRT17. The expression of miRNA-485-5p and KRT17 in PC tissue and cancer cell lines was detected by Q-PCR paired with western blot assay. The biological function of miRNA-485-5p in regulating KRT17 was investigated in the PC cell line via gene silencing/overexpression technique. A western blot experiment was utilized to investigate the regulatory effect of KRT17 on cell cycle-related proteins and the FAK/Src/ERK signal pathway. Results: The level of KRT17 was increased in PC tissues and this significantly decreased the survival rate of PC patients. TargetScan in combination with dual luciferase and RIP experiments verified the miRNA-485-5p target KRT17. The expression of KRT17 was high in the PC cell line, although the expression of miRNA-485-5p was low. Silencing KRT17 or overexpression of miRNA-485-5p significantly inhibited PC cell viability, proliferation, invasion, and colony formation, while promoting apoptosis. Overexpression of KRT17 drastically reversed the function of miRNA-485-5p. The silenced KRT17 remarkably downregulated the expression of cyclinD1, Cyclin Dependent Kinase 1 (CDK1), CDK2, Phospho-Focal Adhesion Kinase (p-FAK), p-Src, and p-ERK proteins in the PC cells. Conclusion: Generally, an essential signaling cascade of miRNA-485-5p/KRT17/FAK/Src/ERK influences the biological functions of PC cells.
Keywords: Cell cycle; KRT17; MiRNA-485-5p; Pancreatic cancer; Proliferation.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-485-5p targets keratin 17 to regulate oral cancer stemness and chemoresistance via the integrin/FAK/Src/ERK/β-catenin pathway.J Biomed Sci. 2022 Jun 15;29(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s12929-022-00824-z. J Biomed Sci. 2022. PMID: 35706019 Free PMC article.
-
KRT17 Functions as a Tumor Promoter and Regulates Proliferation, Migration and Invasion in Pancreatic Cancer via mTOR/S6k1 Pathway.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 Mar 19;12:2087-2095. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S243129. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. PMID: 32256116 Free PMC article.
-
CircCCNB1 silencing acting as a miR-106b-5p sponge inhibited GPM6A expression to promote HCC progression by enhancing DYNC1I1 expression and activating the AKT/ERK signaling pathway.Int J Biol Sci. 2022 Jan 1;18(2):637-651. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.66915. eCollection 2022. Int J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35002514 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA HCP5 Regulates Pancreatic Cancer Progression by miR-140-5p/CDK8 Axis.Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2020 Nov;35(9):711-719. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2019.3294. Epub 2020 May 14. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2020. PMID: 32407143
-
Long non-coding RNA NORAD contributes to the proliferation, invasion and EMT progression of prostate cancer via the miR-30a-5p/RAB11A/WNT/β-catenin pathway.Cancer Cell Int. 2020 Nov 27;20(1):571. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01665-2. Cancer Cell Int. 2020. PMID: 33292272 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Focal adhesion kinase as a new player in the biology of onco-hematological diseases: the starting evidence.Front Oncol. 2024 Aug 30;14:1446723. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1446723. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39281374 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tempero MA. NCCN Guidelines Updates: Pancreatic Cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2019. 17::603-5. - PubMed
-
- Schizas D, Charalampakis N, Kole C, Economopoulou P, Koustas E, Gkotsis E. et al. Immunotherapy for pancreatic cancer: A 2020 update. Cancer Treat Rev. 2020;86:102016. - PubMed
-
- Neoptolemos JP, Kleeff J, Michl P, Costello E, Greenhalf W, Palmer DH. Therapeutic developments in pancreatic cancer: current and future pers pectives. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;15:333–48. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

