Identification of a lncRNA/circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma by deep sequencing and bioinformatics analysis
- PMID: 38434987
- PMCID: PMC10905391
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.91546
Identification of a lncRNA/circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma by deep sequencing and bioinformatics analysis
Abstract
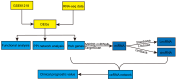
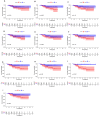
Background: Accumulating evidence indicates that non-coding RNAs (ncRNA), including long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and circular RNAs (circRNAs), can function as competitive endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs) by binding to microRNAs (miRNAs) and regulating host gene expression at the transcriptional or post-transcriptional level. Dysregulation in ceRNA network regulation has been implicated in the occurrence and development of cancer. However, the lncRNA/circRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network is still lacking in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). Methods: Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were obtained from our previous sequencing data and Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO). Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway (KEGG) were used to explore the biological functions of these common DEGs. Through a series of bioinformatic analyses, the lncRNA/circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network was established. In additional, the external data GSE102349 was used to test the prognostic value of the hub mRNAs through the Kaplan-Meier method. Results: We successfully constructed a lncRNA/circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network in NPC, consisting of 16 lncRNAs, 6 miRNAs, 3 circRNAs and 10 mRNAs and found that three genes (TOP2A, ZWINT, TTK) were significantly associated with overall survival time (OS) in patients. Conclusion: The regulatory network revealed in this study may help comprehensively elucidate the ceRNA mechanisms driving NPC, and provide novel candidate biomarkers for evaluating the prognosis of NPC.
Keywords: bioinformatics; competitive endogenous RNA; deep sequencing; nasopharyngeal carcinoma; non-coding RNAs.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures





References
-
- Chang ET, Adami H-O. The Enigmatic Epidemiology of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2006;15:1765–77. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y-P, Chan ATC, Le Q-T, Blanchard P, Sun Y, Ma J. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. The Lancet. 2019;394:64–80. - PubMed
-
- Yuan L, EBV infection-induced GPX4 promotes chemoresistance and tumor progression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cell Death Differ [Internet]. 2022 [cited. 2023. Feb 12];29. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35105963/ - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

