Arthroscopically Assisted Double-Bundle Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Augmentation With Physeal-Sparing Suture Fixation for Recurrent Patellar Dislocation in Skeletally Immature Patients
- PMID: 38435249
- PMCID: PMC10907910
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eats.2023.09.028
Arthroscopically Assisted Double-Bundle Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Augmentation With Physeal-Sparing Suture Fixation for Recurrent Patellar Dislocation in Skeletally Immature Patients
Abstract
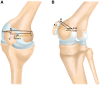
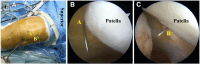
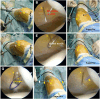
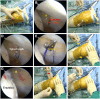
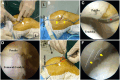
Recurrent patellar dislocation is a common patellofemoral disease that affects active adolescents. The optimal surgical treatment of recurrent patellar dislocation in skeletally immature patients remains controversial. This Technical Note describes an arthroscopically assisted double-bundle medial patellofemoral ligament (MPFL) augmentation. Orthocord suture, with ideal strength and partial bioabsorbable characteristics, is used as the stabilizer to augment and protect the native MPFL during its biological healing. Under an arthroscope, patellar tunnels are created with Kirshner wire at the upper third point of the medial articular margin and the midpoint of the proximal articular margin. A physeal-sparing transosseous suture fixation technique is applied at the femoral attachment. Two femoral tunnels are made with half-circle cutting needle, which is pierced into the femoral origin of the MPFL and exits the posterior femoral cortex. After dynamic assessments of knee range of motion and patellofemoral congruence, free ends of the Orthocord suture bundle are tied together at the external opening of the femoral tunnel. Transosseous suture fixation balances the requirements of anatomic restoration, reliable fixation, and physeal preservation, and thus may provide a promising alternative to current algorithm of addressing recurrent patellar dislocation in pediatric population.
© 2024 Published by Elsevier Inc. on behalf of the Arthroscopy Association of North America.
Figures


References
-
- Gurusamy P., Pedowitz J.M., Carroll A.N., et al. Medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction for adolescents with acute first-time patellar dislocation with an associated loose body. Am J Sports Med. 2021;49:2159–2164. - PubMed
-
- Schlichte L.M., Sidharthan S., Green D.W., Parikh S.N. Pediatric management of recurrent patellar instability. Sports Med Arthrosc Rev. 2019;27:171–180. - PubMed
-
- Scanlon J.P., Raymond A.C., Aujla R.S., et al. Combined quadriceps medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction and osteochondral fixation offers good patient-reported outcomes and low rates of recurrent instability for osteochondral defects secondary to acute patella dislocation. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2023;31:4007–4015. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

