Synergizing language learning: SmallTalk AI In industry 4.0 and Education 4.0
- PMID: 38435575
- PMCID: PMC10909197
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj-cs.1843
Synergizing language learning: SmallTalk AI In industry 4.0 and Education 4.0
Abstract
Background: As Industry 4.0 debuted roughly a decade ago, it is now necessary to examine how it affects various aspects of the discipline. It is the responsibility of the education sector to guarantee that the next generation is equipped mentally, physically, and cognitively to face unforeseen challenges. Numerous educational institutions are outfitted with Industry 4.0 technology-based learning. Industry 4.0 fosters advancements in learning methodologies, especially for language enhancements. Learners may gain knowledge at their base, providing them an opportunity for independent study. The majority of subjects have been acquired through Industry 4.0. This research chapter explores the intersection of Industry 4.0 and education, specifically focusing on the SmallTalk AI tool. It investigates how technological and digital innovations within the context of Industry 4.0 can serve as powerful tools to enhance language learning outcomes.
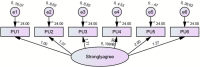
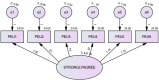
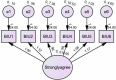
Methods: This article presents a comprehensive analysis of statistical data and empirical evidence to support the positive impact of Industry 4.0 technology of SmallTalk on language acquisition particularly speaking. The study also determines the relationship among participants' usage through the technology acceptance model (TAM). Furthermore, it examines the challenges and opportunities associated with integrating these innovations into language learning pedagogies, offering insights for educators and policymakers to harness the potential of Industry 4.0 in fostering language proficiency. The research employs quantitative analysis. The data obtained from educational institutions has been analyzed using the SPSS and AMOS software.
Results: The results indicate that Industry 4.0 has had an important effect on English language acquisition. This self-supported adaptable system of education facilitates effective student learning. This study also suggests that future research into the utility of Industry 4.0 be conducted elsewhere internationally.
Keywords: Education; Education 4.0; Industry 4.0; Language acquisition; Language learning; SmallTalk AI; TAM.
©2024 Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Bao Y, Zhang Y, Wang J, Luo L. Investigating the effectiveness of online language learning: A meta-analysis of empirical studies. Computers & Education. 2020;145:103729. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2019.103729. - DOI
-
- Brown SR, Lee J. Mobile-assisted language learning: a comparative analysis of language learners’ engagement and achievement. Journal of Educational Technology & Society. 2017;20(3):133–144.
-
- Chan CK, Loh JY. Industry 4.0 and language education: opportunities and challenges. Journal of Applied Research in Higher Education. 2019;11(3):507–519.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials