The Relationship Between UA/HDL and Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: A Cross-Sectional Analysis
- PMID: 38435629
- PMCID: PMC10908281
- DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S447809
The Relationship Between UA/HDL and Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: A Cross-Sectional Analysis
Abstract
Purpose: This study was designed to analyze correlations between the uric acid to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (UHR) and peripheral nerve conduction velocity (NCV) among type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients.
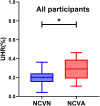
Patients and methods: This was a single-center cross-sectional analysis of 324 T2DM patients. All patients were separated into a group with normal NCV (NCVN) and a group with abnormal NCV (NCVA). Patients were also classified into groups with low and high UHR values based on the median UHR in this study cohort. Neurophysiological data including motor and sensory conduction velocity (MCV and SCV, respectively) were measured for all patients.
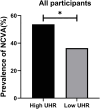
Results: Relative to patients with low UHR values, those in the high UHR group presented with greater NCVA prevalence (P = 0.002). UHR remained negatively correlated with bilateral superficial peroneal nerve SCV, bilateral common peroneal nerve MCV, bilateral ulnar nerve SCV, and bilateral right median nerve MCV even after adjustment for confounding factors. UHR was identified as an NCVA-related risk factor, with a 1.370-fold increase in NCVA prevalence for every unit rise in UHR (P < 0.001).
Conclusion: These results identify UHR as a risk factor associated with NCVA that was independently negatively associated with NCV among T2DM patients.
Keywords: diabetic peripheral neuropathy; peripheral nerve conduction velocity; type 2 diabetes mellitus; uric acid to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio.
© 2024 Zhen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Correlation Between Hemoglobin Glycosylation Index and Nerve Conduction Velocity in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2021 Dec 4;14:4757-4765. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S334767. eCollection 2021. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2021. PMID: 34887673 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation Between Thioredoxin-Interacting Protein and Nerve Conduction Velocity in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Front Neurol. 2020 Jul 22;11:733. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00733. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32774321 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation Between Fibrinogen/Albumin and Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2023 Sep 27;16:2991-3005. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S427510. eCollection 2023. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2023. PMID: 37790261 Free PMC article.
-
[Systematic review and Meta-analysis of efficacy and safety of Shuxuetong Injection in treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022 Jun;47(11):3088-3094. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20220303.501. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35718533 Chinese.
-
[Systematic review and Meta-analysis of efficacy and safety of Tangmaikang Granules in treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023 Jan;48(2):542-554. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20220926.502. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 36725244 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Correlation Between the Ratio of Uric Acid to High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (UHR) and Diabetic Retinopathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus:A Cross-Sectional Study.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2025 Jan 20;18:173-183. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S504308. eCollection 2025. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2025. PMID: 39866522 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

