Critical factors driving spatiotemporal variability in the phytoplankton community structure of the coral habitat in Dongshan Bay, China
- PMID: 38435699
- PMCID: PMC10904553
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1355028
Critical factors driving spatiotemporal variability in the phytoplankton community structure of the coral habitat in Dongshan Bay, China
Abstract
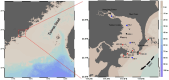
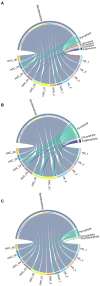
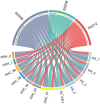
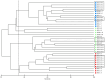
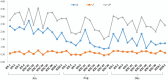
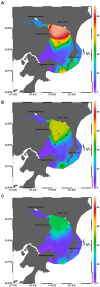
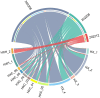
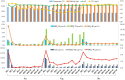
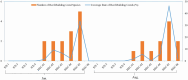
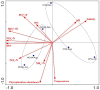
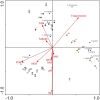
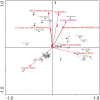
This study investigated the spatiotemporal distribution of the phytoplankton in the coral habitat of Dongshan Bay (China), along with critical factors affecting the distribution, during June, August, and December 2022. Phytoplankton abundance in Dongshan Bay exhibited considerably temporal variation, peaking in June 2022, gradually decreasing thereafter, and reaching its lowest point in December 2022. The abundance of bottom-layer phytoplankton consistently exceeded that of the surface layer throughout all seasons. The average phytoplankton abundance in the coral habitat of Dongshan Bay was lower than that in non-coral habitat areas. Fluctuations in the Zhangjiang River and coastal upwelling influenced the diversity and community structure of the phytoplankton. Critical factors causing spatiotemporal variability in phytoplankton community structure included nutrient concentrations and seawater temperature. Nutrients played key roles in influencing various phytoplankton groups. Dominant diatom species, such as Thalassionema nitzschioides and Thalassiosira diporocyclus, were positively correlated with ammonia nitrogen, seawater salinity, coral cover, and the number of coral species present. In winter, Calanus sinicus exhibited a negative correlation with harmful algal bloom species. Additionally, it was found that both in the coral habitat and surrounding open sea, currents, nutrients, and zooplankton may play crucial roles in determining the spatiotemporal variability in the phytoplankton community structure.
Keywords: community structure; coral habitat; current; nutrient; phytoplankton; spatiotemporal variability.
Copyright © 2024 Zhou, Dong, Wang, Ye, Yang, Xiang, Chen and Zheng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Community composition of phytoplankton in Fujian-Guangdong coastal upwelling region in summer and related affecting factors].Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2011 Feb;22(2):503-12. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2011. PMID: 21608268 Chinese.
-
Investigating the impacts of treated effluent discharge on coastal water health (Visakhapatnam, SW coast of Bay of Bengal, India).Environ Monit Assess. 2017 Nov 21;189(12):643. doi: 10.1007/s10661-017-6344-1. Environ Monit Assess. 2017. PMID: 29164356
-
Long-term changes in summer phytoplankton communities and their influencing factors in Daya Bay, China (1991-2017).Mar Pollut Bull. 2020 Dec;161(Pt A):111694. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111694. Epub 2020 Oct 2. Mar Pollut Bull. 2020. PMID: 33017701
-
[Annual change of phytoplankton ecological features in Fangchenggang Bay of Guangxi, South China].Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2011 May;22(5):1309-15. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2011. PMID: 21812311 Chinese.
-
[Effects of Pollution Control of Xiaoqing River on Environment Factors and Phytoplankton Community in the Laizhou Bay].Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2022 Apr 8;43(4):1997-2006. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202108128. Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2022. PMID: 35393823 Chinese.
References
-
- Bizani M., Bornman T. G., Campbell E. E., Perissinotto R., Deyzel S. H. P. (2023). Mesozooplankton community responses to a large-scale harmful algal bloom induced by the non-indigenous dinoflagellate Lingulodinium polyedra. Sci. Total Environ. 860:161030. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.161030, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen J., Fu Z., Li F. (1982). A study of upwelling over Minnan-Taiwan shoal fishing ground. Taiwan Strait 1, 5–13.
-
- Chen Y.-H., Gao Y.-H., Chen C.-P., Liang J.-R., Sun L., Zhen Y., et al. . (2016). Seasonal variations of phytoplankton assemblages and its relation to environmental variables in a scallop culture sea area of Bohai Bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 113, 362–370. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.10.025, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen B., Ji W., Zhou K., He Q., Fu T. (2014). Nutrient and eutrophication characteristics of the Dongshan Bay, South China. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 32, 886–898. doi: 10.1007/s00343-014-3214-3 - DOI
-
- Chen B., Wang K., Peng C., Dong X., Wang S., Lin H. (2023). Changes of eutrophication degree in Dongshan Bay in China affected by the COVID-19 outbreak. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 66:103119. doi: 10.1016/j.rsma.2023.103119 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

