The number of previous implantation failures is a critical determinant of intrauterine autologous platelet-rich plasma infusion success in women with recurrent implantation failure
- PMID: 38435746
- PMCID: PMC10904764
- DOI: 10.1002/rmb2.12565
The number of previous implantation failures is a critical determinant of intrauterine autologous platelet-rich plasma infusion success in women with recurrent implantation failure
Abstract
Purpose: We aimed to identify factors influencing the reproductive outcomes of frozen-thawed embryo transfer (FET) with intrauterine autologous platelet-rich plasma (PRP) infusion in patients with either a thin endometrium or recurrent implantation failure (RIF) despite a normal endometrial appearance.
Methods: In this retrospective study of women who underwent PRP-FET, factors influencing PRP-FET outcomes were identified using multivariate logistic regression analysis.
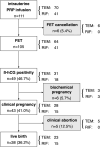
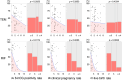
Results: We enrolled 111 patients (70 with refractory thin endometrium and 41 with RIF but no thin endometrium). For 99 completed FET cycles, the β-hCG positivity rate was 46.7%, clinical pregnancy rate (CPR) was 41.0%, and live birth rate (LBR) was 36.2%. PRP treatment was associated with significant improvements over previous cycles, and participants with thin endometria demonstrated thickening. Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that the number of previous implantation failures in women with RIF was a significant factor affecting the PRP-FET outcomes. The CPR and LBR of women with RIF were lower when there had been ≥3 previous implantation failures occurred.
Conclusions: Intrauterine PRP infusion improves the pregnancy outcomes of patients with RIF or a thin endometrium. The number of previous implantation failures is a critical determinant of successful intrauterine PRP infusions in women with RIF.
Keywords: embryo implantation; embryo transfer; endometrium; infertility; platelet‐rich plasma.
© 2024 The Authors. Reproductive Medicine and Biology published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japan Society for Reproductive Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of autologous platelet-rich plasma intrauterine perfusion on clinical outcomes in recurrent implantation failure patients with non-thin endometrium undergoing frozen-thawed embryo transfer.Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2025 May;311(5):1423-1433. doi: 10.1007/s00404-025-07983-y. Epub 2025 Mar 19. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2025. PMID: 40105934 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma Treatment on Refractory Thin Endometrium During the Frozen Embryo Transfer Cycle: A Pilot Study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019 Feb 14;10:61. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00061. eCollection 2019. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019. PMID: 30837945 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of endometrial PRP on fertility outcomes in women with implantation failure or thin endometrium.Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2025 Apr;311(4):1195-1204. doi: 10.1007/s00404-025-07948-1. Epub 2025 Feb 13. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2025. PMID: 39939464 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of intrauterine infusion of platelet-rich plasma for women with recurrent implantation failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Obstet Gynaecol. 2023 Dec;43(1):2144177. doi: 10.1080/01443615.2022.2144177. Epub 2022 Nov 17. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2023. PMID: 36397660
-
Intrauterine infusion of autologous platelet-rich plasma in women undergoing assisted reproduction: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Reprod Immunol. 2020 Feb;137:103078. doi: 10.1016/j.jri.2019.103078. Epub 2019 Dec 31. J Reprod Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32006776
Cited by
-
Efficacy of intrauterine autologous blood cell derivatives in enhancing endometrial thickness and IVF outcomes for women with recurrent implantation failure: a retrospective cohort study.J Assist Reprod Genet. 2024 Oct;41(10):2667-2680. doi: 10.1007/s10815-024-03231-5. Epub 2024 Sep 5. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2024. PMID: 39235518 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive single-cell transcriptome analysis of autologous platelet-rich plasma therapy on human thin endometrium.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 26;15(1):14637. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-99468-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40287476 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kasius A, Smit JG, Torrance HL, Eijkemans MJ, Mol BW, Opmeer BC, et al. Endometrial thickness and pregnancy rates after IVF: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Hum Reprod Update. 2014;20(4):530–541. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
