ZNF692 Promotes the Progression of Colon Adenocarcinoma by Regulating HSF4 Expression
- PMID: 38435777
- PMCID: PMC10903307
- DOI: 10.18502/ijph.v52i12.14321
ZNF692 Promotes the Progression of Colon Adenocarcinoma by Regulating HSF4 Expression
Abstract
Background: Colon adenocarcinoma (COAD) is one of the most common cancer happened in gastrointestinal tract, with the overall incidence rate of 4%-5% among human beings. Like most malignancies, we uncovered the exact mechanisms of the pathogenesis of colorectal cancer yet. Therefore, there is an urgent need to explore the molecules that can be used as diagnostic maker at early stage. In addition, we also need to define the essential factors that related to the prognosis and treatment of the colon carcinoma.
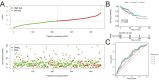
Methods: The study was conducted at the Third Affiliated Hospital of Qiqihar Medical University, Qiqihar, China in September 2020. The R language was used to identify the differentially expressed genes. We performed receiver operating characteristic curve analysis to determine the diagnostic markers for COAD. The machine learning strategy was used to assess the effectiveness of genes in the diagnosis of COAD. The molecular mechanism and prognostic value of genes were explored by bioinformatics analysis and molecular experiments.
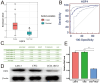
Results: The expression level of heat shock factor 4 (HSF4) was significantly elevated in COAD patients (P=1.89×10-29), according to The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. Additionally, survival analysis showed the higher expression level of the HSF4 was correlated with the poor prognosis in COAD.
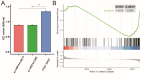
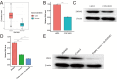
Conclusion: The HSF4 was the target gene of zinc finger protein 692(ZNF692). HSF4 might promote the progression of COAD through the apoptosis pathway. It was diagnostic and prognosis maker of COAD. Furthermore, the upstream gene of HSF4, ZNF692, promotes the progression of colorectal cancer by regulating HSF4 expression.
Keywords: Biomarker; Colon adenocarcinoma; Heat shock factor 4; Zinc finger protein 692.
Copyright© 2023 Yang et al. Published by Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Figures
Similar articles
-
High Expression of MORC2 is Associated with Poor Clinical Outcomes and Immune Infiltrates in Colon Adenocarcinoma.Int J Gen Med. 2023 Oct 11;16:4595-4615. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S420715. eCollection 2023. Int J Gen Med. 2023. PMID: 37850194 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic and prognostic potential of the novel biomarker nuclear cap binding protein subunit 2 (NCBP2) in colon adenocarcinoma.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022 Aug;13(4):1782-1792. doi: 10.21037/jgo-22-665. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36092349 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA ALMS1-IT1 is a novel prognostic biomarker and correlated with immune infiltrates in colon adenocarcinoma.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Oct 21;101(42):e31314. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000031314. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36281164 Free PMC article.
-
A potential prognostic prediction model of colon adenocarcinoma with recurrence based on prognostic lncRNA signatures.Hum Genomics. 2020 Jun 10;14(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s40246-020-00270-8. Hum Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32522293 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Transcription Factor-Related Gene Signature and Risk Score Model for Colon Adenocarcinoma.Front Genet. 2021 Sep 17;12:709133. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.709133. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34603375 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Targeting Heat Shock Transcription Factor 4 Enhances the Efficacy of Cabozantinib and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Renal Cell Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 19;26(4):1776. doi: 10.3390/ijms26041776. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40004241 Free PMC article.
-
Zinc Finger Proteins in Colorectal Cancer: Insights into Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2025 Jan-Dec;24:15330338251334447. doi: 10.1177/15330338251334447. Epub 2025 Apr 10. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2025. PMID: 40208082 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
