Micro Trojan horses: Engineering extracellular vesicles crossing biological barriers for drug delivery
- PMID: 38435823
- PMCID: PMC10905561
- DOI: 10.1002/btm2.10623
Micro Trojan horses: Engineering extracellular vesicles crossing biological barriers for drug delivery
Abstract
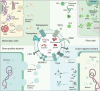
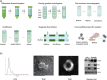
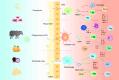
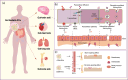
The biological barriers of the body, such as the blood-brain, placental, intestinal, skin, and air-blood, protect against invading viruses and bacteria while providing necessary physical support. However, these barriers also hinder the delivery of drugs to target tissues, reducing their therapeutic efficacy. Extracellular vesicles (EVs), nanostructures with a diameter ranging from 30 nm to 10 μm secreted by cells, offer a potential solution to this challenge. These natural vesicles can effectively pass through various biological barriers, facilitating intercellular communication. As a result, artificially engineered EVs that mimic or are superior to the natural ones have emerged as a promising drug delivery vehicle, capable of delivering drugs to almost any body part to treat various diseases. This review first provides an overview of the formation and cross-species uptake of natural EVs from different organisms, including animals, plants, and bacteria. Later, it explores the current clinical applications, perspectives, and challenges associated with using engineered EVs as a drug delivery platform. Finally, it aims to inspire further research to help bioengineered EVs effectively cross biological barriers to treat diseases.
Keywords: biological barriers; drug delivery; engineering; extracellular vesicles; therapy.
© 2024 The Authors. Bioengineering & Translational Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Institute of Chemical Engineers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Engineered Extracellular Vesicles for Drug Delivery in Therapy of Stroke.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Aug 22;15(9):2173. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15092173. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37765144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles: Novel promising delivery systems for therapy of brain diseases.J Control Release. 2017 Sep 28;262:247-258. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.07.001. Epub 2017 Jul 4. J Control Release. 2017. PMID: 28687495 Review.
-
Cellular Uptake of Engineered Extracellular Vesicles: Biomechanisms, Engineered Strategies, and Disease Treatment.Adv Healthc Mater. 2024 Jan;13(2):e2302280. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202302280. Epub 2023 Oct 26. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024. PMID: 37812035 Review.
-
Engineered Extracellular Vesicles as a Targeted Delivery Platform for Precision Therapy.Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2023 Apr;20(2):157-175. doi: 10.1007/s13770-022-00503-y. Epub 2023 Jan 13. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2023. PMID: 36637750 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicle- and Extracellular Vesicle Mimetics-Based Drug Delivery Systems: New Perspectives, Challenges, and Clinical Developments.Pharmaceutics. 2020 May 11;12(5):442. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12050442. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 32403320 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bioinspired cellular membrane-derived vesicles for mRNA delivery.Theranostics. 2024 May 19;14(8):3246-3266. doi: 10.7150/thno.93755. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 38855184 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine: Perspectives and Challenges.MedComm (2020). 2025 Apr 24;6(5):e70192. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70192. eCollection 2025 May. MedComm (2020). 2025. PMID: 40290901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles as delivery vehicles and therapeutic agents for glioblastoma treatment: A systematic review of in vitro and in vivo preclinical studies.Asian J Pharm Sci. 2025 Jun;20(3):101043. doi: 10.1016/j.ajps.2025.101043. Epub 2025 Mar 14. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2025. PMID: 40503055 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological and Bioinspired Vesicles for Wound Healing: Insights, Advances and Challenges.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Jun 30;20:8497-8528. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S522067. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40620685 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles as Tools for Crossing the Blood-Brain Barrier to Treat Lysosomal Storage Diseases.Life (Basel). 2025 Jan 9;15(1):70. doi: 10.3390/life15010070. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39860010 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Harris‐Tryon TA, Grice EA. Microbiota and maintenance of skin barrier function. Science. 2022;376:940‐945. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

