The toxicity assessment of phosmet on development, reproduction, and gene expression in Daphnia magna
- PMID: 38436013
- PMCID: PMC10908259
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.17034
The toxicity assessment of phosmet on development, reproduction, and gene expression in Daphnia magna
Abstract
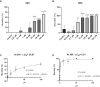
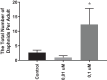
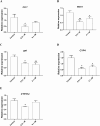
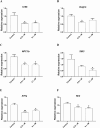
The use of pesticides to control pests, weeds, and diseases or to regulate plant growth is indispensable in agricultural production. However, the excessive use of these chemicals has led to significant concern about their potential negative impacts on health and the environment. Phosmet is one such pesticide that is commonly used on plants and animals against cold moth, aphids, mites, suckers, and fruit flies. Here, we investigated the effects of phosmet on a model organism, Daphnia magna using acute and chronic toxicity endpoints such as lethality, mobility, genotoxicity, reproduction, and gene expression. We performed survival experiments in six-well plates at seven different concentrations (0.01, 0.1, 1, 10, 25, 50, 100 μM) as well as the control in three replicates. We observed statistically significant mortality rates at 25 µM and above upon 24 h of exposure, and at 1 µM and above following 48 h of exposure. Genotoxicity analysis, reproduction assay and qPCR analysis were carried out at concentrations of 0.01 and 0.1 μM phosmet as these concentrations did not show any lethality. Comet assay showed that exposure to phosmet resulted in significant DNA damage in the cells. Interestingly, 0.1 μM phosmet produced more offspring per adult compared to the control group indicating a hormetic response. Gene expression profiles demonstrated several genes involved in different physiological pathways, including oxidative stress, detoxification, immune system, hypoxia and iron homeostasis. Taken together, our results indicate that phosmet has negative effects on Daphnia magna in a dose- and time-dependent manner and could also induce lethal and physiological toxicities to other aquatic organisms.
Keywords: Comet assay; Daphnia magna; Gene expression; Phosmet; Reproduction.
© 2024 Ataş and Bereketoglu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Toxic effects of environmentally relevant concentrations of naproxen exposure on Daphnia magna including antioxidant system, development, and reproduction.Aquat Toxicol. 2024 Jan;266:106794. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2023.106794. Epub 2023 Dec 7. Aquat Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38064890
-
Evaluation of modes of action of pesticides to Daphnia magna based on QSAR, excess toxicity and critical body residues.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2020 Oct 15;203:111046. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111046. Epub 2020 Jul 24. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2020. PMID: 32888614
-
Comparative toxicity of rac- and S-tebuconazole to Daphnia magna.J Environ Sci Health B. 2015;50(7):456-62. doi: 10.1080/03601234.2015.1018756. J Environ Sci Health B. 2015. PMID: 25996809
-
Effects of polyvinyl chloride microplastics on reproduction, oxidative stress and reproduction and detoxification-related genes in Daphnia magna.Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2022 Apr;254:109269. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpc.2022.109269. Epub 2022 Jan 11. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35026397
-
Daphnia magna model in the toxicity assessment of pharmaceuticals: A review.Sci Total Environ. 2021 Apr 1;763:143038. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143038. Epub 2020 Oct 16. Sci Total Environ. 2021. PMID: 33127157 Review.
References
-
- Anastassiadou M, Arena M, Auteri D, Brancato A, Bura L, Carrasco Cabrera L, Chaideftou E, Chiusolo A, Crivellente F, De Lentdecker C, Egsmose M, Fait G, Greco L, Ippolito A, Istace F, Jarrah S, Kardassi D, Leuschner R, Lostia A, Lythgo C, Magrans O, Mangas I, Miron I, Molnar T, Padovani L, Parra Morte JM, Pedersen R, Reich H, Santos M, Sharp R, Szentes C, Terron A, Tiramani M, Vagenende B, Villamar-Bouza L. Peer review of the pesticide risk assessment of the active substance phosmet. EFSA Journal. 2021;19(3):e06237. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2021.6237. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benson WH, Di Giulio RT. Sediment Toxicity Assessment. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 2018. Biomarkers in hazard assessments of contaminated sediments; pp. 241–265.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

