A combination of genomics and transcriptomics provides insights into the distribution and differential mRNA expression of type VI secretion system in clinical Klebsiella pneumoniae
- PMID: 38436228
- PMCID: PMC10964426
- DOI: 10.1128/msphere.00822-23
A combination of genomics and transcriptomics provides insights into the distribution and differential mRNA expression of type VI secretion system in clinical Klebsiella pneumoniae
Abstract
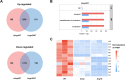
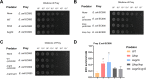
The type VI secretion system (T6SS) serves as a crucial molecular weapon in interbacterial competition and significantly influences the adaptability of bacteria in their ecological niche. However, the distribution and function of T6SS in clinical Klebsiella pneumoniae, a common opportunistic nosocomial pathogen, have not been fully elucidated. Here, we conducted a genomic analysis of 65 clinical K. pneumoniae isolates obtained from patients with varying infections. Genes encoding a T6SS cluster present in all analyzed strains of K. pneumoniae, and strains with identical sequence type carried structurally and numerically identical T6SS. Our study also highlights the importance of selecting conserved regions within essential T6SS genes for PCR-based identification of T6SS in bacteria. Afterward, we utilized the predominant sequence type 11 (ST11) K. pneumoniae HS11286 to investigate the effect of knocking out T6SS marker genes hcp or vgrG. Transcriptome analysis identified a total of 1,298 co-upregulated and 1,752 co-downregulated differentially expressed genes in both mutants. Pathway analysis showed that only Δhcp mutant exhibited alterations in transport, establishment of localization, localization, and cell processes. The absence of hcp or vgrG gene suppressed the expression of other T6SS-related genes within the locus I cluster. Additionally, interbacterial competition experiments showed that hcp and vgrG are essential for competitive ability of ST11 K. pneumoniae HS11286. This study furthers our understanding of the genomic characteristics of T6SS in clinical K. pneumoniae and suggests the involvement of multiple genes in T6SS of strain HS11286.
Importance: Gram-negative bacteria use type VI secretion system (T6SS) to deliver effectors that interact with neighboring cells for niche advantage. Klebsiella pneumoniae is an opportunistic nosocomial pathogen that often carries multiple T6SS loci, the function of which has not yet been elucidated. We performed a genomic analysis of 65 clinical K. pneumoniae strains isolated from various sources, confirming that all strains contained T6SS. We then used transcriptomics to further study changes in gene expression and its effect on interbacterial competition following the knockout of key T6SS genes in sequence type 11 (ST11) K. pneumoniae HS11286. Our findings revealed the distribution and genomic characteristics of T6SS in clinical K. pneumoniae. This study also described the overall transcriptional changes in the predominant Chinese ST11 strain HS11286 upon deletion of crucial T6SS genes. Additionally, this work provides a reference for future research on the identification of T6SS in bacteria.
Keywords: Klebsiella pneumoniae; genomic; transcriptomic; type VI secretion system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Insights into Klebsiella pneumoniae type VI secretion system transcriptional regulation.BMC Genomics. 2019 Jun 18;20(1):506. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-5885-9. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31215404 Free PMC article.
-
A Quorum Sensing-Regulated Type VI Secretion System Containing Multiple Nonredundant VgrG Proteins Is Required for Interbacterial Competition in Chromobacterium violaceum.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Aug 31;10(4):e0157622. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01576-22. Epub 2022 Jul 25. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35876575 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Characterization of an Antibacterial Type VI Secretion System in the Carbapenem-Resistant Strain Klebsiella pneumoniae HS11286.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Oct 12;7:442. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00442. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29085808 Free PMC article.
-
The Biological and Regulatory Role of Type VI Secretion System of Klebsiella pneumoniae.Infect Drug Resist. 2023 Oct 30;16:6911-6922. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S426657. eCollection 2023. Infect Drug Resist. 2023. PMID: 37928603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
T6SS in plant pathogens: unique mechanisms in complex hosts.Infect Immun. 2024 Sep 10;92(9):e0050023. doi: 10.1128/iai.00500-23. Epub 2024 Aug 21. Infect Immun. 2024. PMID: 39166846 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epidemiological and genetic charateristics of Vibrio vulnificus from diverse sources in China during 2012-2023.Commun Biol. 2025 Jan 4;8(1):9. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-07426-5. Commun Biol. 2025. PMID: 39755764 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
