[In vitro expression and functional analyses of the mutants p.R243Q, p.R241C and p.Y356X of the human phenylalanine hydroxylase]
- PMID: 38436318
- PMCID: PMC10921879
- DOI: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2309035
[In vitro expression and functional analyses of the mutants p.R243Q, p.R241C and p.Y356X of the human phenylalanine hydroxylase]
Abstract
Objectives: To study the in vitro expression of three phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) mutants (p.R243Q, p.R241C, and p.Y356X) and determine their pathogenicity.
Methods: Bioinformatics techniques were used to predict the impact of PAH mutants on the structure and function of PAH protein. Corresponding mutant plasmids of PAH were constructed and expressed in HEK293T cells. Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction was used to measure the mRNA expression levels of the three PAH mutants, and their protein levels were assessed using Western blot and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
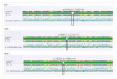
Results: Bioinformatics analysis predicted that all three mutants were pathogenic. The mRNA expression levels of the p.R243Q and p.R241C mutants in HEK293T cells were similar to the mRNA expression level of the wild-type control (P>0.05), while the mRNA expression level of the p.Y356X mutant significantly decreased (P<0.05). The PAH protein expression levels of all three mutants were significantly reduced compared to the wild-type control (P<0.05). The extracellular concentration of PAH protein was reduced in the p.R241C and p.Y356X mutants compared to the wild-type control (P<0.05), while there was no significant difference between the p.R243Q mutant and the wild type control (P>0.05).
Conclusions: p.R243Q, p.R241C and p.Y356X mutants lead to reduced expression levels of PAH protein in eukaryotic cells, with p.R241C and p.Y356X mutants also affecting the function of PAH protein. These three PAH mutants are to be pathogenic.
目的: 分析3种苯丙氨酸羟化酶(phenylalanine hydroxylase, PAH)突变体(p.R243Q、p.R241C和p.Y356X)的体外表达,确定3种突变体的致病性。方法: 利用生物信息学技术预测PAH突变体对PAH蛋白结构和功能的影响。构建相应的PAH突变型质粒,在人胚胎肾细胞HEK293T中进行表达,采用定量逆转录聚合酶链反应检测3种PAH突变体的mRNA表达水平,利用蛋白质印迹法与酶联免疫吸附试验检测突变体的PAH蛋白表达水平。结果: 生物信息学分析预测结果显示,3种突变体均具备致病性。突变体p.R243Q和p.R241C质粒在HEK293T细胞中的mRNA表达水平与野生型类似(P>0.05),而p.Y356X突变体质粒的mRNA表达水平明显下降(P<0.05)。3种突变体PAH蛋白的表达水平与野生型相比均显著降低(P<0.05)。p.R241C和p.Y356X的细胞外PAH蛋白浓度较野生型降低(P<0.05),p.R243Q与野生型相比差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。结论: p.R243Q、p.R241C和p.Y356X降低真核细胞中PAH蛋白的表达量,其中p.R241C和p.Y356X还影响PAH蛋白的功能,这3种PAH突变体均为致病性突变。.
Keywords: Cell; In vitro expression; Mutant; Phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency.
Conflict of interest statement
所有作者声明无利益冲突。
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Genotype and phenotype correlation of phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency among patients from Henan].Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2016 Jun;33(3):300-5. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1003-9406.2016.03.005. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27264808 Chinese.
-
Three novel variants (p.Glu178Lys, p.Val245Met, p.Ser250Phe) of the phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) gene impair protein expression and function in vitro.Gene. 2018 Aug 20;668:135-139. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.03.078. Epub 2018 Apr 10. Gene. 2018. PMID: 29653233
-
Structural and functional analyses of mutations of the human phenylalanine hydroxylase gene.Clin Chim Acta. 2006 Mar;365(1-2):279-87. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2005.09.019. Epub 2005 Oct 25. Clin Chim Acta. 2006. PMID: 16253218
-
Tetrahydrobiopterin-responsive phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency, state of the art.Mol Genet Metab. 2003 Feb;78(2):93-9. doi: 10.1016/s1096-7192(02)00229-9. Mol Genet Metab. 2003. PMID: 12618080 Review.
-
How PAH gene mutations cause hyper-phenylalaninemia and why mechanism matters: insights from in vitro expression.Hum Mutat. 2003 Apr;21(4):357-69. doi: 10.1002/humu.10197. Hum Mutat. 2003. PMID: 12655545 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources