High remnant cholesterol as a risk factor for developing chronic kidney disease in patients with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes: a cross-sectional study of a US population
- PMID: 38436703
- PMCID: PMC11101368
- DOI: 10.1007/s00592-024-02249-6
High remnant cholesterol as a risk factor for developing chronic kidney disease in patients with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes: a cross-sectional study of a US population
Erratum in
-
Correction to: High remnant cholesterol as a risk factor for developing chronic kidney disease in patients with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes: a cross-sectional study of a US population.Acta Diabetol. 2024 Jun;61(6):745. doi: 10.1007/s00592-024-02274-5. Acta Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 38625393 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Aims: To examine any potential links between remnant cholesterol (RC) and comorbid chronic kidney disease (CKD) in individuals with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods: We used data from 2709 American people aged > 20 years from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) during 2011-2018. Subjects were categorized according to whether they had comorbid CKD. Logistic regression models and smoothed curve fitting methods were employed to assess the association of RC with comorbid CKD in patients with prediabetes and T2DM.
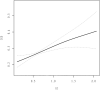
Results: The 2709 participants included 1473 patients with T2DM and 1236 with prediabetes [impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) and impaired fasting glucose (IFG)], of whom 744 (27.46%) had comorbid CKD. In multivariate-adjusted analysis, both RC and triglycerides (TG) were significantly associated with an increased risk of comorbid CKD, and a 1 mmol/L elevation of RC increased the risk by 38.1% [OR (95% CI) 1.636 (1.242, 2.156)], which was higher than the risk associated with a 1 mmol/L increase in TG [1.255 (1.106, 1.424)]. Additionally, those in the highest quartile of RC had a 43.6% higher risk of concomitant renal damage than those in the lowest quartile. RC was linearly and positively associated with the incidence of comorbid CKD in this population.
Conclusions: RC is an independent risk factor for comorbid CKD in patients with prediabetes and T2DM. This finding provides a novel insight into the management and early detection of renal disease in patients with impaired glucose metabolism.
Keywords: Chronic kidney disease; NHANES; Prediabetes; Remnant cholesterol; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Association between remnant cholesterol and chronic kidney disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2025 May;27(5):2573-2583. doi: 10.1111/dom.16258. Epub 2025 Feb 14. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2025. PMID: 39950216 Free PMC article.
-
Remnant cholesterol, preinflammatory state and chronic kidney disease: association and mediation analyses.Ren Fail. 2024 Dec;46(2):2361094. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2024.2361094. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Ren Fail. 2024. PMID: 38856016 Free PMC article.
-
Association of remnant cholesterol with chronic kidney disease in middle-aged and elderly Chinese: a population-based study.Acta Diabetol. 2021 Dec;58(12):1615-1625. doi: 10.1007/s00592-021-01765-z. Epub 2021 Jun 28. Acta Diabetol. 2021. PMID: 34181081
-
Prevalence of Prediabetes Among Adolescents and Young Adults in the United States, 2005-2016.JAMA Pediatr. 2020 Feb 1;174(2):e194498. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2019.4498. Epub 2020 Feb 3. JAMA Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 31790544 Free PMC article.
-
Prediabetes and CKD: Does a causal relationship exist.Nefrologia (Engl Ed). 2024 Sep-Oct;44(5):628-638. doi: 10.1016/j.nefroe.2024.11.005. Nefrologia (Engl Ed). 2024. PMID: 39547776 Review.
Cited by
-
Correlation between conventional and unconventional lipid parameters with the risk of progression of renal function decline: insights from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study 2011-2015.Ren Fail. 2025 Dec;47(1):2499229. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2025.2499229. Epub 2025 May 7. Ren Fail. 2025. PMID: 40336192 Free PMC article.
-
Association between remnant cholesterol and chronic kidney disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2025 May;27(5):2573-2583. doi: 10.1111/dom.16258. Epub 2025 Feb 14. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2025. PMID: 39950216 Free PMC article.
-
Association between lymphocyte to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome in US adults: results from NHANES 2007-2018.Lipids Health Dis. 2025 Jan 10;24(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02411-7. Lipids Health Dis. 2025. PMID: 39794792 Free PMC article.
-
Remnant cholesterol, preinflammatory state and chronic kidney disease: association and mediation analyses.Ren Fail. 2024 Dec;46(2):2361094. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2024.2361094. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Ren Fail. 2024. PMID: 38856016 Free PMC article.
-
Trends, Social Determinants, and Lifestyle Factors Associated With Comorbidity of Diabetes and Kidney Diseases Among Chinese Adults Aged ≥ 45 Years.J Diabetes. 2025 Aug;17(8):e70142. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.70142. J Diabetes. 2025. PMID: 40814743 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Spijkerman AM, Dekker JM, Nijpels G, et al. Microvascular complications at time of diagnosis of type 2 diabetes are similar among diabetic patients detected by targeted screening and patients newly diagnosed in general practice: the hoorn screening study. Diabetes Care. 2003;26:2604–2608. doi: 10.2337/diacare.26.9.2604. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

