Comparison of surgical and oncological outcomes between different surgical approaches for overweight or obese cervical cancer patients
- PMID: 38436785
- PMCID: PMC10912340
- DOI: 10.1007/s11701-024-01863-4
Comparison of surgical and oncological outcomes between different surgical approaches for overweight or obese cervical cancer patients
Abstract
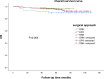
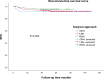
The purpose was to investigate the safety and advantages of different surgical approaches applied to overweight or obese cervical cancer patients by comparing their surgical and oncological outcomes. This is a retrospective cohort study. 382 patients with a body mass index of at least 24.0 kg/m2 and stage IB-IIA (The International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics, FIGO 2009) cervical cancer were enrolled, and then were divided into three groups: open radical hysterectomy (ORH) group, laparoscopic radical hysterectomy (LRH) group, and robot-assisted radical hysterectomy (RRH) group according to the surgical approach. IBM SPSS version 25.0 was used to analyze data. There were 51 patients in ORH group, 225 patients in LRH group and 106 patients in RRH group. In the comparison of surgical outcomes, compared to LRH and ORH, RRH had the shortest operating time, the least estimated blood loss, the shortest postoperative hospital stay, and the shortest recovery time for bowel function (P < 0.05). In the comparison of postoperative complications, ORH has the highest rate of postoperative infection and wound complication compared to LRH and RRH (P < 0.05), and RRH has the highest proportion of urinary retention. After a median follow-up time of 61 months, there was no statistically significant difference between the three groups in terms of 5-year overall survival (OS) rate and 5-year recurrence-free survival (RFS) rate, (P = 0.262, P = 0.453). In patients with overweight or obese cervical cancer, the long-term outcomes of the three surgical approaches were comparable, with RRH showing significant advantages over ORH and LRH in terms of surgical outcomes.
Keywords: Cervical cancer; Complications; Obesity; Outcomes; Radical total hysterectomy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Survival rate comparisons amongst cervical cancer patients treated with an open, robotic-assisted or laparoscopic radical hysterectomy: A five year experience.Surg Oncol. 2016 Mar;25(1):66-71. doi: 10.1016/j.suronc.2015.09.004. Epub 2015 Sep 14. Surg Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26409687
-
Meta-analysis of laparoscopic radical hysterectomy, excluding robotic assisted versus open radical hysterectomy for early stage cervical cancer.Sci Rep. 2023 Jan 6;13(1):273. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-27430-9. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36609438 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and safety outcomes of robotic radical hysterectomy in Chinese older women with cervical cancer compared with laparoscopic radical hysterectomy.BMC Womens Health. 2018 May 1;18(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s12905-018-0544-x. BMC Womens Health. 2018. PMID: 29716555 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical comparative study of robot-assisted and traditional laparoscopic surgery in patients with cervical cancer: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Surg. 2024 Dec 27;24(1):423. doi: 10.1186/s12893-024-02716-5. BMC Surg. 2024. PMID: 39731015 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the complications between minimally invasive surgery and open surgical treatments for early-stage cervical cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2021 Jul 1;16(7):e0253143. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0253143. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34197466 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cervical cancer. https://www.iarc.who.int/cancer-type/cervical-cancer/. Accessed 2023
-
- Ramirez PT, Frumovitz M, Pareja R et al (2018) Minimally invasive versus abdominal radical hysterectomy for cervical cancer. N Engl J Med 379(20):1895–1904 - PubMed
-
- Jungles KM, Green MD (2022) Fat fuels the fire in cervical cancer. Cancer Res 82(24):4513–4514 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- cstc2021jcyj-msxmX0120/Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing,China
- cstc2021jcyj-msxmX0120/Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing,China
- cstc2021jcyj-msxmX0120/Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing,China
- cstc2021jcyj-msxmX0120/Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing,China
- cstc2021jcyj-msxmX0120/Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing,China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical