Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia with hepatic arteriovenous shunt diagnosed due to liver damage
- PMID: 38436842
- PMCID: PMC11127884
- DOI: 10.1007/s12328-024-01923-0
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia with hepatic arteriovenous shunt diagnosed due to liver damage
Abstract
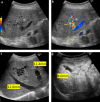
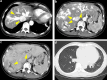
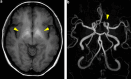
A 53-year-old woman was diagnosed with liver dysfunction in August 20XX. Computed tomography (CT) revealed multiple hepatic AV shunts, and she was placed under observation. In March 20XX + 3, she developed back pain, and CT performed during an emergency hospital visit showed evidence of intrahepatic bile duct dilatation. She was referred to our gastroenterology department in May 20XX + 3. We conducted investigations on suspicion of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT) with hepatic AV shunting based on contrast-enhanced CT performed at another hospital. HHT is generally discovered due to epistaxis, but there are also cases where it is diagnosed during examination of liver damage.
Keywords: Hepatic arteriovenous shunt; Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia; Liver damage.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Masatoshi Kudo received patent royalties from Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Masatoshi Kudo received scholarship grants from Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., TAIHO Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., GE Healthcare Japan Corporation and Eisai Co., Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Osler W. On a family form of recurring epistaxis, associated with multiple telangiectases of the skin and mucous membranes. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1901;128:333–337.
-
- Hanes F. Multiple hereditary telangiectases causing hemorrhage (hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia) Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1909;20:63–73.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

