Mini-Puberty, Physiological and Disordered: Consequences, and Potential for Therapeutic Replacement
- PMID: 38436980
- PMCID: PMC11244267
- DOI: 10.1210/endrev/bnae003
Mini-Puberty, Physiological and Disordered: Consequences, and Potential for Therapeutic Replacement
Abstract
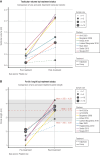
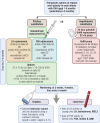
There are 3 physiological waves of central hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis activity over the lifetime. The first occurs during fetal life, the second-termed "mini-puberty"-in the first months after birth, and the third at puberty. After adolescence, the axis remains active all through adulthood. Congenital hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (CHH) is a rare genetic disorder characterized by a deficiency in hypothalamic gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) secretion or action. In cases of severe CHH, all 3 waves of GnRH pulsatility are absent. The absence of fetal HPG axis activation manifests in around 50% of male newborns with micropenis and/or undescended testes (cryptorchidism). In these boys, the lack of the mini-puberty phase accentuates testicular immaturity. This is characterized by a low number of Sertoli cells, which are important for future reproductive capacity. Thus, absent mini-puberty will have detrimental effects on later fertility in these males. The diagnosis of CHH is often missed in infants, and even if recognized, there is no consensus on optimal therapeutic management. Here we review physiological mini-puberty and consequences of central HPG axis disorders; provide a diagnostic approach to allow for early identification of these conditions; and review current treatment options for replacement of mini-puberty in male infants with CHH. There is evidence from small case series that replacement with gonadotropins to mimic "mini-puberty" in males could have beneficial outcomes not only regarding testis descent, but also normalization of testis and penile sizes. Moreover, such therapeutic replacement regimens in disordered mini-puberty could address both reproductive and nonreproductive implications.
Keywords: Kallmann syndrome; congenital hypogonadotropic hypogonadism; cryptorchidism; gonadotropins; hypogonadism; infancy; micropenis; mini-puberty; puberty.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society.
Figures




References
-
- Kaplan SL, Grumbach MM. The ontogenesis of human foetal hormones. II. Luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH). Acta Endocrinol (Norway). 1976;81(4):808‐829. - PubMed
-
- Johannsen TH, Main KM, Ljubicic ML, et al. Sex differences in reproductive hormones during mini-puberty in infants with normal and disordered sex development. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;103(8):3028‐3037. - PubMed
-
- Massa G, de Zegher F, Vanderschueren-Lodeweyckx M. Serum levels of immunoreactive inhibin, FSH, and LH in human infants at preterm and term birth. Biol Neonate. 1992;61(3):150‐155. - PubMed
-
- Mannan MA, O'Shaughnessy PJ. Steroidogenesis during postnatal development in the mouse ovary. J Endocrinol. 1991;130(1):101-NP. - PubMed
-
- Herbison AE. The gonadotropin-releasing hormone pulse generator. Endocrinology. 2018;159(11):3723‐3736. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

