Two host-plant strains in the fall armyworm
- PMID: 38437152
- PMCID: PMC11632296
- DOI: 10.1111/1744-7917.13346
Two host-plant strains in the fall armyworm
Abstract
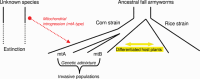
The fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda) is one of the major pest insects damaging diverse crops including cotton, corn, rice, and sorghum. Fall armyworms have been identified as two morphologically indistinguishable strains, the corn strain, and the rice strain, named after their preferred host-plants. Although initially recognized as host-plant strains, there has been an ongoing debate regarding whether the corn and rice strains should be considered as such. In this article, we present arguments based on recent population genomics studies supporting that these two strains should be considered to be host-plant strains. Furthermore, host-plant adaptation appears to be a driving evolutionary force responsible for incipient speciation in the fall armyworm.
Keywords: Spodoptera frugiperda; fall armyworm; host‐plant adaptation; incipient speciation.
© 2024 The Authors. Insect Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Barton, N.H. (1979) Gene flow past a cline. Heredity, 43, 333–339.
-
- Barton, N.H. (1983) Multilocus clines. Evolution; International Journal of Organic Evolution, 37, 454–471. - PubMed
-
- Blanco, C.A. , Portilla, M. , Jurat‐Fuentes, J.L. , Sánchez, J.F. , Viteri, D. , Vega‐Aquino, P. , et al. (2010) Susceptibility of isofamilies of Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) to Cry1Ac and Cry1Fa proteins of Bacillus thuringiensis . Southwestern Entomologist, 35, 409–416.
-
- Cañas‐Hoyos, N. , Lobo‐Echeverri, T. and Saldamando‐Benjumea, C.I. (2017) Chemical composition of female sexual glands of Spodoptera frugiperda corn and rice strains from Tolima, Colombia. Southwestern Entomologist, 42, 375–394.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

