Motivators and barriers to the acceptability of a human milk bank among Malaysians
- PMID: 38437241
- PMCID: PMC10911625
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0299308
Motivators and barriers to the acceptability of a human milk bank among Malaysians
Abstract
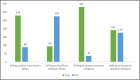
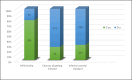
The World Health Organisation (WHO) recommends that all babies be exclusively breastfed, stating that donor milk is the next best alternative in the absence of the mother's own milk. Milk sharing takes many forms, namely wet nursing, co-feeding, cross-feeding, and a human milk bank (HMB). However, the establishment of a human milk bank is still not widely accepted and is a debatable topic because of religious concerns in Malaysia. The aim of this study is to determine the facilitators and barriers among Malaysians towards the acceptance of an HMB. A cross-sectional study with 367 participants was conducted; the participants answered an online-validated, self-administered questionnaire. Data on sociodemographic, knowledge on breastfeeding benefits, knowledge and attitude on HMB-specific issues were analysed in terms of frequency before proceeded with multiple logistic regression. The majority of the respondents were Muslim (73.3%), had completed their tertiary education (82.8%), and were employed (70.8%). Only 55.9% of respondents had heard of HMB, stating the internet as their main source of information, but many respondents were agreeable to its establishment (67.8%). Most respondents had a good score on knowledge of breastfeeding benefits and on HMB-specific issues (70% and 54.2%, respectively), while 63.8% had a positive attitude towards HMB. In the multivariate analysis, mothers with a good score on general knowledge of breastfeeding (AOR: 1.715; 95% CI 1.047-2.808) were more likely to accept the establishment of HMB, while being a Muslim was negatively associated with its establishment (AOR = 0.113, 95% CI 0.050-0.253). The study found a high prevalence of mothers who were willing to accept the establishment of HMB. By educating mothers on the benefits of breastfeeding, as well as addressing their religious concerns, the establishment of a religiously abiding HMB in Malaysia may be accepted without compromising their beliefs or the health benefit of donor milk.
Copyright: © 2024 Ramachandran et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
No authors have competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Attitudes towards human milk banking among native turkish and refugee women residing in a rural region of Turkey: a mixed-methods approach.Int Breastfeed J. 2022 Oct 27;17(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s13006-022-00516-2. Int Breastfeed J. 2022. PMID: 36303181 Free PMC article.
-
Human milk banking and milk kinship: Perspectives of mothers in a Muslim country.J Trop Pediatr. 2015 Jun;61(3):188-96. doi: 10.1093/tropej/fmv018. Epub 2015 Mar 30. J Trop Pediatr. 2015. PMID: 25828832
-
Postpartum women's views on human milk banking in a city in Southeast China: a cross-sectional survey.Int Breastfeed J. 2022 Jan 7;17(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s13006-021-00443-8. Int Breastfeed J. 2022. PMID: 34991642 Free PMC article.
-
The global status of human milk banking.Matern Child Nutr. 2024 Jun;20 Suppl 4(Suppl 4):e13592. doi: 10.1111/mcn.13592. Epub 2024 Feb 6. Matern Child Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38318679 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Factors Influencing Donations to Human Milk Bank: A Systematic Review of Facilitators and Barriers.Breastfeed Med. 2019 Jun;14(5):298-306. doi: 10.1089/bfm.2019.0002. Epub 2019 Mar 21. Breastfeed Med. 2019. PMID: 30896254
Cited by
-
Donate or Not to Donate-Willingness to Donate and Accept Donor Human Milk.Nutrients. 2025 Jul 18;17(14):2359. doi: 10.3390/nu17142359. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40732983 Free PMC article.
-
Bridging the Milk Gap: Integrating a Human Milk Bank-Blood Bank Model to Reinforce Lactation Support and Neonatal Care.Nutrients. 2025 May 23;17(11):1765. doi: 10.3390/nu17111765. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40507034 Free PMC article.
-
Donor human milk practice in Indonesia: a media content analysis.Front Nutr. 2024 Sep 18;11:1442864. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1442864. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39360271 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources