Thiophene-based lipids for mRNA delivery to pulmonary and retinal tissues
- PMID: 38437570
- PMCID: PMC10945828
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2307813120
Thiophene-based lipids for mRNA delivery to pulmonary and retinal tissues
Abstract
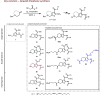
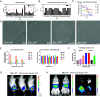
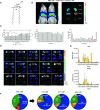
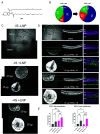
Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) largely rely on ionizable lipids to yield successful nucleic acid delivery via electrostatic disruption of the endosomal membrane. Here, we report the identification and evaluation of ionizable lipids containing a thiophene moiety (Thio-lipids). The Thio-lipids can be readily synthesized via the Gewald reaction, allowing for modular lipid design with functional constituents at various positions of the thiophene ring. Through the rational design of ionizable lipid structure, we prepared 47 Thio-lipids and identified some structural criteria required in Thio-lipids for efficient mRNA (messenger RNA) encapsulation and delivery in vitro and in vivo. Notably, none of the tested lipids have a pH-response profile like traditional ionizable lipids, potentially due to the electron delocalization in the thiophene core. Placement of the tails and localization of the ionizable headgroup in the thiophene core can endow the nanoparticles with the capability to reach various tissues. Using high-throughput formulation and barcoding techniques, we optimized the formulations to select two top lipids-20b and 29d-and investigated their biodistribution in mice. Lipid 20b enabled LNPs to transfect the liver and spleen, and 29d LNP transfected the lung and spleen. Unexpectedly, LNP with lipid 20b was especially potent in mRNA delivery to the retina with no acute toxicity, leading to the successful delivery to the photoreceptors and retinal pigment epithelium in non-human primates.
Keywords: ionizable lipid; lipid nanoparticle; mRNA delivery.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:Y.E., M. Gupta, J.K., M. Gautam, J.R., and G.S. are inventors on a patent application pertinent to this work filed by the Oregon State University. Y.E., D.N., and A.T. have stock options and advisory roles with EnterX Bio. G.S. is a cofounder of EnterX Bio. EnterX Bio has a scientific research agreement with Oregon State University. G.S. has a conflict management plan at Oregon State University. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

