Environmental radon, fracking wells, and lymphoma in dogs
- PMID: 38437620
- PMCID: PMC11099769
- DOI: 10.1111/jvim.17021
Environmental radon, fracking wells, and lymphoma in dogs
Abstract
Background: Multicentric lymphoma (ML) in dogs resembles non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) in humans. Human NHL is associated with multiple environmental exposures, including to radon and volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
Hypothesis/objectives: The objective of this study was to determine whether ML in dogs was associated with environmental radon or proximity to horizontal oil and drilling (fracking), a source of VOC pollution.
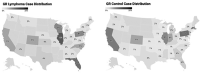
Methods: We identified dogs from the Golden Retriever Lifetime Study that developed ML (n = 52) along with matched controls (n = 104). Dog home addresses were categorized by Environmental Protection Agency radon zone and average residential radon by county, as well as by distance from fracking and associated wastewater wells.
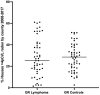
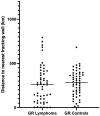
Results: We found no significant differences in county level radon measurements. Individual household radon measurements were not available. There was no difference in residential proximity to active fracking wells between dogs with ML and unaffected dogs. While dogs with ML lived closer to wastewater wells (123 vs 206 km; P = .01), there was no difference in the percentage of cases vs controls that lived in close proximity (20 km) to a fracking well (11.5% for cases, 6.7% for controls; OR 1.81, 95% CI 0.55 to 5.22; P = .36), or a wastewater well (6.7% for cases, 4.4% for controls; P > .99).
Conclusions and clinical importance: These data suggest that more proximate sources of chemical exposures need to be assessed in dogs with ML, including measurements of individual household radon and household VOC concentrations.
Keywords: class II injection wells; fracking; horizontal drilling; multicentric lymphoma; non‐Hodgkin lymphoma; volatile organic compounds; wastewater.
© 2024 The Authors. Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American College of Veterinary Internal Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Lauren A. Trepanier serves as Associate Editor for the Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine. She was not involved in review of this manuscript. Lauren A. Trepanier is on the Scientific Advisory Board for the Morris Animal Foundation but has no direct involvement in the Golden Retriever Lifetime Study. No other authors declare a conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Bronden LB, Nielsen SS, Toft N, Kristensen AT. Data from the Danish veterinary cancer registry on the occurrence and distribution of neoplasms in dogs in Denmark. Vet Rec. 2010;166(19):586‐590. - PubMed
-
- Zandvliet M. Canine lymphoma: a review. Vet Q. 2016;36(2):76‐104. - PubMed
-
- Teske E. Canine malignant lymphoma: a review and comparison with human non‐Hodgkin's lymphoma. Vet Q. 1994;16(4):209‐219. - PubMed
-
- Gavazza A, Presciuttini S, Barale R, Lubas G, Gugliucci B. Association between canine malignant lymphoma, living in industrial areas, and use of chemicals by dog owners. J Vet Intern Med. 2001;15(3):190‐195. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

