Hardware implementation of memristor-based artificial neural networks
- PMID: 38438350
- PMCID: PMC10912231
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-45670-9
Hardware implementation of memristor-based artificial neural networks
Abstract
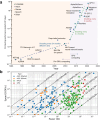
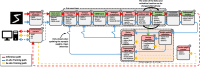
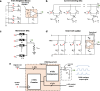
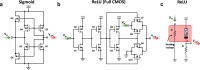
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is currently experiencing a bloom driven by deep learning (DL) techniques, which rely on networks of connected simple computing units operating in parallel. The low communication bandwidth between memory and processing units in conventional von Neumann machines does not support the requirements of emerging applications that rely extensively on large sets of data. More recent computing paradigms, such as high parallelization and near-memory computing, help alleviate the data communication bottleneck to some extent, but paradigm- shifting concepts are required. Memristors, a novel beyond-complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) technology, are a promising choice for memory devices due to their unique intrinsic device-level properties, enabling both storing and computing with a small, massively-parallel footprint at low power. Theoretically, this directly translates to a major boost in energy efficiency and computational throughput, but various practical challenges remain. In this work we review the latest efforts for achieving hardware-based memristive artificial neural networks (ANNs), describing with detail the working principia of each block and the different design alternatives with their own advantages and disadvantages, as well as the tools required for accurate estimation of performance metrics. Ultimately, we aim to provide a comprehensive protocol of the materials and methods involved in memristive neural networks to those aiming to start working in this field and the experts looking for a holistic approach.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





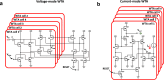




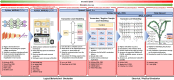


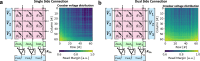

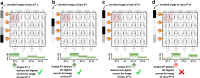
References
-
- European Commission, Harnessing the economic benefits of Artificial Intelligence. Digital Transformation Monitor, no. November, 8, 2017.
-
- Rattani, A. Reddy, N. and Derakhshani, R. “Multi-biometric Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile User Authentication,” 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Technologies for Homeland Security, HST 2018, 10.1109/THS.2018.8574173 2018.
-
- BBVA, Biometrics and machine learning: the accurate, secure way to access your bank Accessed: Jan. 21, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.bbva.com/en/biometrics-and-machine-learning-the-accurate-sec...
-
- Amerini I, Li C-T, Caldelli R. Social network identification through image classification with CNN. IEEE Access. 2019;7:35264–35273. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2903876. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

