Detecting stochastic multiresonance in neural networks via statistical complexity measure
- PMID: 38438571
- PMCID: PMC10912744
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-55997-4
Detecting stochastic multiresonance in neural networks via statistical complexity measure
Abstract
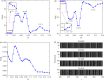
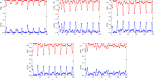
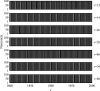
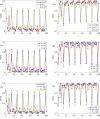
This paper employs statistical complexity measure (SCM) to investigate the occurrence of stochastic multiresonance (SMR) induced by noise and time delay in small-world neural networks coupled with FitzHugh-Nagumo (FHN) neurons. Our findings reveal that SCM exhibits four local maxima at four optimal noise levels, providing evidence for the occurrence of quadruple stochastic resonances. When time delay is taken into account in the information transmission, under moderate noise levels, SCM shows several local maxima when with being a positive integer and being the period of subthreshold signal. This indicates the appearance of delay-induced SMR at the multiples of the period of subthreshold signal. Intriguingly, at low noise levels, a strong coherence between time delay and neuronal firing dynamics emerges at , as confirmed by a series of SCM maxima at these time delays. Furthermore, the study demonstrates that by adjusting the degrees and sizes of small-world networks, as well as the coupling strength, it is possible to optimize the strength of delay-induced SMR, thus maximizing the detection capability of subthreshold signal. The research results may provide us with an effective approach for understanding the role of time delay in signal detection and information transmission.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Stochastic multiresonance in coupled excitable FHN neurons.Chaos. 2018 Apr;28(4):043113. doi: 10.1063/1.4997679. Chaos. 2018. PMID: 31906634
-
Effects of time delay on the stochastic resonance in small-world neuronal networks.Chaos. 2013 Mar;23(1):013128. doi: 10.1063/1.4790829. Chaos. 2013. PMID: 23556965
-
Transition from double coherence resonances to single coherence resonance in a neuronal network with phase noise.Chaos. 2015 Dec;25(12):123124. doi: 10.1063/1.4938733. Chaos. 2015. PMID: 26723163
-
Effects of time delay and random rewiring on the stochastic resonance in excitable small-world neuronal networks.Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2013 May;87(5):052917. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.87.052917. Epub 2013 May 28. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2013. PMID: 23767608
-
Lag synchronization of coupled time-delayed FitzHugh-Nagumo neural networks via feedback control.Sci Rep. 2021 Feb 16;11(1):3884. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-82886-x. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33594138 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benzi R, Sutera A, Vulpiani A. The mechanism of stochastic resonance. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 1981;14:L453. doi: 10.1088/0305-4470/14/11/006. - DOI
-
- Xu PF, Jin YF. Stochastic resonance in an asymmetric tristable system driven by correlated noises. Appl. Math. Model. 2020;77:408–425. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2019.07.053. - DOI
-
- Lu SL, He QB, Wang J. A review of stochastic resonance in rotating machine fault detection. Mech. Syst. Signal. Pr. 2019;116:230–260. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2018.06.032. - DOI
-
- Shi ZZ, Liao ZQ, Tabata H. Boosting learning ability of overdamped bistable stochastic resonance system based physical reservoir computing model by time-delayed feedback. Chaos Soliton. Fract. 2022;161:112314. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2022.112314. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

