Single-cell guided prenatal derivation of primary fetal epithelial organoids from human amniotic and tracheal fluids
- PMID: 38438734
- PMCID: PMC10957479
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-024-02807-z
Single-cell guided prenatal derivation of primary fetal epithelial organoids from human amniotic and tracheal fluids
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Single-cell guided prenatal derivation of primary fetal epithelial organoids from human amniotic and tracheal fluids.Nat Med. 2025 Feb;31(2):699. doi: 10.1038/s41591-025-03504-1. Nat Med. 2025. PMID: 39838120 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
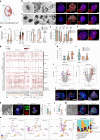
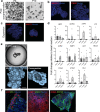
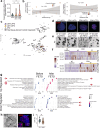
Isolation of tissue-specific fetal stem cells and derivation of primary organoids is limited to samples obtained from termination of pregnancies, hampering prenatal investigation of fetal development and congenital diseases. Therefore, new patient-specific in vitro models are needed. To this aim, isolation and expansion of fetal stem cells during pregnancy, without the need for tissue samples or reprogramming, would be advantageous. Amniotic fluid (AF) is a source of cells from multiple developing organs. Using single-cell analysis, we characterized the cellular identities present in human AF. We identified and isolated viable epithelial stem/progenitor cells of fetal gastrointestinal, renal and pulmonary origin. Upon culture, these cells formed clonal epithelial organoids, manifesting small intestine, kidney tubule and lung identity. AF organoids exhibit transcriptomic, protein expression and functional features of their tissue of origin. With relevance for prenatal disease modeling, we derived lung organoids from AF and tracheal fluid cells of congenital diaphragmatic hernia fetuses, recapitulating some features of the disease. AF organoids are derived in a timeline compatible with prenatal intervention, potentially allowing investigation of therapeutic tools and regenerative medicine strategies personalized to the fetus at clinically relevant developmental stages.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The views expressed are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the NHS, the NIHR or the Department of Health. The authors declare the following competing interests: a patent detailing the AFO technology was filed by UCL on 18 April 2023 entitled ‘Derivation of Primary Organoids from the Fetal Fluids’, under application no. GB2305703.7. M.F.M.G., G.G.G., P.D.C. and G.C. are listed as inventors on the patent. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures











References
-
- Senat, M.-V. et al. Endoscopic laser surgery versus serial amnioreduction for severe twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med.351, 136–144 (2004). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

