Associations of plasma proteomics and age-related outcomes with brain age in a diverse cohort
- PMID: 38438772
- PMCID: PMC11226584
- DOI: 10.1007/s11357-024-01112-4
Associations of plasma proteomics and age-related outcomes with brain age in a diverse cohort
Abstract
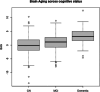
Machine learning models are increasingly being used to estimate "brain age" from neuroimaging data. The gap between chronological age and the estimated brain age gap (BAG) is potentially a measure of accelerated and resilient brain aging. Brain age calculated in this fashion has been shown to be associated with mortality, measures of physical function, health, and disease. Here, we estimate the BAG using a voxel-based elastic net regression approach, and then, we investigate its associations with mortality, cognitive status, and measures of health and disease in participants from Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study who had a brain MRI at visit 5 of the study. Finally, we used the SOMAscan assay containing 4877 proteins to examine the proteomic associations with the MRI-defined BAG. Among N = 1849 participants (age, 76.4 (SD 5.6)), we found that increased values of BAG were strongly associated with increased mortality and increased severity of the cognitive status. Strong associations with mortality persisted when the analyses were performed in cognitively normal participants. In addition, it was strongly associated with BMI, diabetes, measures of physical function, hypertension, prevalent heart disease, and stroke. Finally, we found 33 proteins associated with BAG after a correction for multiple comparisons. The top proteins with positive associations to brain age were growth/differentiation factor 15 (GDF-15), Sushi, von Willebrand factor type A, EGF, and pentraxin domain-containing protein 1 (SEVP 1), matrilysin (MMP7), ADAMTS-like protein 2 (ADAMTS), and heat shock 70 kDa protein 1B (HSPA1B) while EGF-receptor (EGFR), mast/stem-cell-growth-factor-receptor (KIT), coagulation-factor-VII, and cGMP-dependent-protein-kinase-1 (PRKG1) were negatively associated to brain age. Several of these proteins were previously associated with dementia in ARIC. These results suggest that circulating proteins implicated in biological aging, cellular senescence, angiogenesis, and coagulation are associated with a neuroimaging measure of brain aging.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Brain age; Machine learning; Mortality; Proteomics.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Is an MRI-derived anatomical measure of dementia risk also a measure of brain aging?Geroscience. 2023 Feb;45(1):439-450. doi: 10.1007/s11357-022-00650-z. Epub 2022 Sep 2. Geroscience. 2023. PMID: 36050589 Free PMC article.
-
Biological brain age and resilience in cognitively unimpaired 70-year-old individuals.Alzheimers Dement. 2025 Feb;21(2):e14435. doi: 10.1002/alz.14435. Epub 2024 Dec 20. Alzheimers Dement. 2025. PMID: 39704304 Free PMC article.
-
MRI or 18F-FDG PET for Brain Age Gap Estimation: Links to Cognition, Pathology, and Alzheimer Disease Progression.J Nucl Med. 2024 Jan 2;65(1):147-155. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.123.265931. J Nucl Med. 2024. PMID: 38050112 Free PMC article.
-
Structural magnetic resonance imaging for the early diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer's disease in people with mild cognitive impairment.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Mar 2;3(3):CD009628. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009628.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32119112 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging Janus face of SVEP1 in development and disease.Trends Mol Med. 2023 Nov;29(11):939-950. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2023.08.002. Epub 2023 Sep 4. Trends Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37673700 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cardiometabolic risk factors and brain age: a meta-analysis to quantify brain structural differences related to diabetes, hypertension, and obesity.J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2025 Mar 11;50(2):E102-E111. doi: 10.1503/jpn.240105. Print 2025 Mar-Apr. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40068862 Free PMC article.
-
Radiomic and proteomic signatures of body mass index on brain ageing and Alzheimer's-like patterns of brain atrophy.EBioMedicine. 2025 Jun;116:105763. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2025.105763. Epub 2025 May 27. EBioMedicine. 2025. PMID: 40435724 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetes, Prediabetes, and Brain Aging: The Role of Healthy Lifestyle.Diabetes Care. 2024 Oct 1;47(10):1794-1802. doi: 10.2337/dc24-0860. Diabetes Care. 2024. PMID: 39193914 Free PMC article.
-
Brain age prediction from MRI scans in neurodegenerative diseases.Curr Opin Neurol. 2025 Aug 1;38(4):316-321. doi: 10.1097/WCO.0000000000001383. Epub 2025 May 21. Curr Opin Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40396549 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

