Transfer learning-based PET/CT three-dimensional convolutional neural network fusion of image and clinical information for prediction of EGFR mutation in lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 38438844
- PMCID: PMC10913633
- DOI: 10.1186/s12880-024-01232-5
Transfer learning-based PET/CT three-dimensional convolutional neural network fusion of image and clinical information for prediction of EGFR mutation in lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Background: To introduce a three-dimensional convolutional neural network (3D CNN) leveraging transfer learning for fusing PET/CT images and clinical data to predict EGFR mutation status in lung adenocarcinoma (LADC).
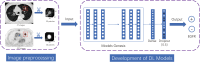
Methods: Retrospective data from 516 LADC patients, encompassing preoperative PET/CT images, clinical information, and EGFR mutation status, were divided into training (n = 404) and test sets (n = 112). Several deep learning models were developed utilizing transfer learning, involving CT-only and PET-only models. A dual-stream model fusing PET and CT and a three-stream transfer learning model (TS_TL) integrating clinical data were also developed. Image preprocessing includes semi-automatic segmentation, resampling, and image cropping. Considering the impact of class imbalance, the performance of the model was evaluated using ROC curves and AUC values.
Results: TS_TL model demonstrated promising performance in predicting the EGFR mutation status, with an AUC of 0.883 (95%CI = 0.849-0.917) in the training set and 0.730 (95%CI = 0.629-0.830) in the independent test set. Particularly in advanced LADC, the model achieved an AUC of 0.871 (95%CI = 0.823-0.919) in the training set and 0.760 (95%CI = 0.638-0.881) in the test set. The model identified distinct activation areas in solid or subsolid lesions associated with wild and mutant types. Additionally, the patterns captured by the model were significantly altered by effective tyrosine kinase inhibitors treatment, leading to notable changes in predicted mutation probabilities.
Conclusion: PET/CT deep learning model can act as a tool for predicting EGFR mutation in LADC. Additionally, it offers clinicians insights for treatment decisions through evaluations both before and after treatment.
Keywords: Deep learning; radiomics; Epidermal growth factor receptor; Lung adenocarcinoma; Positron emission tomography/computed tomography.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- McLoughlin EM, Gentzler RD. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutations. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2020;30(2):127–136. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- ZD202109/Major Project of Changzhou Health Commission
- CM20193010/Key Laboratory of Changzhou High-tech Research Project
- CZQM2020012/Young Talent Development Plan of Changzhou Health Commission
- 2022260/2022 Changzhou 14th Five-Year Plan Health and Health High-level Talent Training Project-Top-notch talents
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

