TonEBP/NFAT5 expression is associated with cisplatin resistance and migration in macrophage-induced A549 cells
- PMID: 38438872
- PMCID: PMC10913585
- DOI: 10.1186/s12860-024-00502-y
TonEBP/NFAT5 expression is associated with cisplatin resistance and migration in macrophage-induced A549 cells
Abstract
Background: Macrophages promote angiogenesis, metastasis, and drug resistance in several cancers. Similarly, TonEBP/NFAT5 induces metastasis in renal carcinoma and colon cancer cells. However, the role of this transcription factor and that of macrophages in lung cancer cells remains unclear. Therefore, this study investigated the effects of macrophages and TonEBP/NFAT5 expression on cisplatin resistance and migration in A549 lung adenocarcinoma cells.
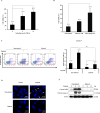
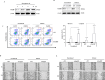
Results: A549 cells were cultured alone or indirectly co-cultured with THP-1-derived macrophages using a transwell culture chamber. Cisplatin-induced cell death was markedly decreased and migration increased in co-cultured A549 cells. Macrophage-conditioned media (CM) showed a similar effect on drug resistance and migration. Cisplatin-induced apoptosis, DNA fragmentation, and cleaved apoptotic proteins PARP and caspase-3 were markedly reduced in macrophage CM-induced A549 cells. Here, ERK, p38, JNK, and NF-κB activities were increased by macrophage CM. Furthermore, the proteins involved in cisplatin resistance and cancer cell migration were identified using specific inhibitors of each protein. ERK and NF-κB inhibition considerably reduced cisplatin resistance. The increase in macrophage CM-induced migration was partially reduced by treatment with ERK, JNK, and NF-κB inhibitors. TonEBP/NFAT5 expression was increased by macrophages, resulting in increased cisplatin resistance, cell migration, and invasion. Moreover, RNAi-mediated knockdown of TonEBP/NFAT5 reduced cisplatin resistance, migration, and invasion in macrophage CM-induced A549 cells.
Conclusions: These findings demonstrate that paracrine factors secreted from macrophages can change A549 cells, resulting in the induction of drug resistance against cisplatin and migration. In addition, the TonEBP/NFAT5 ratio, increased by macrophages, is an important regulator of the malignant transformation of cells.
Keywords: A549; Cisplatin resistance; Migration; TonEBP/NFAT5.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal AJC. Cancer statistics, 2014. 2014;64(1):9–29. - PubMed
-
- Ceresoli GL, Cappuzzo F, Gregorc V, Bartolini S, Crino L, Villa EJAO. Gefitinib in patients with brain metastases from non-small-cell lung cancer: a prospective trial. 2004;15(7):1042–7. - PubMed
-
- Reck M, Popat S, Reinmuth N, De Ruysscher D, Kerr K, Peters SJA. Metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC): ESMO Clinical Practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. 2014;25:iii27–iii39. - PubMed
-
- Wang G, Reed E, Li QQJO. Molecular basis of cellular response to cisplatin chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer. 2004;12(5):955–65. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

