A preliminary study of IgG4 expression and its prognostic significance in oral squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 38438903
- PMCID: PMC10913618
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-024-12048-5
A preliminary study of IgG4 expression and its prognostic significance in oral squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: IgG4, which plays a pivotal role in the progression of phenotypically diverse tumors, serves as a prognostic marker because of its influence on cancer immunity. Nevertheless, the functions of IgG4 in tongue squamous cell carcinoma (TSCC) remained to be identified.
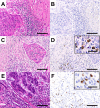
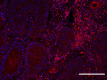
Methods: To evaluate the significance of IgG4 expression in TSCC, we performed immunohistochemical analysis of patients with TSCC (n = 50) to evaluate the correlation of IgG4 expression with patients' clinicopathological features and prognoses.
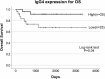
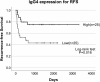
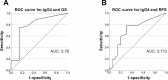
Results: Higher IgG4 expression detected in TSCC tissues was associated with the less advanced mode of invasion (Yamamoto-Kohama [YK] 1-3) (P = 0.031) and with well-differentiated TSCC (P = 0.077). Kaplan-Meier analyses revealed that the higher IgG4 expression group exhibited better prognosis indicated by overall survival (OS) (P = 0.04) and recurrence-free survival (RFS) (P = 0.016). Univariate analysis of OS indicated that IgG4 expression was associated with longer OS (P = 0.061), and multivariate analysis of RFS revealed that IgG4 expression served as an independent prognostic factor for longer RFS (P = 0.005).
Conclusion: These results indicate that relatively higher IgG4 levels serve as a favorable prognostic factor for TSCC.
Keywords: Favorable prognostic factor; IgG4; Tongue squamous cell carcinoma.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CRBP-1 over-expression is associated with poor prognosis in tongue squamous cell carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2018 May 2;18(1):514. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4249-1. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29720147 Free PMC article.
-
Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of PD-1/PD-L1 axis expression in patients with tongue squamous cell carcinoma.J Cell Physiol. 2020 Oct;235(10):6942-6953. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29590. Epub 2020 Feb 6. J Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32030768
-
Overexpression of Hippo pathway effector TAZ in tongue squamous cell carcinoma: correlation with clinicopathological features and patients' prognosis.J Oral Pathol Med. 2013 Nov;42(10):747-54. doi: 10.1111/jop.12062. Epub 2013 Mar 29. J Oral Pathol Med. 2013. PMID: 23551691
-
Progress in the study of long noncoding RNA in tongue squamous cell carcinoma.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2020 Jan;129(1):51-58. doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2019.08.011. Epub 2019 Sep 2. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2020. PMID: 31611036 Review.
-
MicroRNAs in human tongue squamous cell carcinoma: From pathogenesis to therapeutic implications.Oral Oncol. 2017 Apr;67:124-130. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2017.02.015. Epub 2017 Feb 27. Oral Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28351566 Review.
References
-
- Ogino S, Nosho K, Irahara N, Meyerhardt JA, Baba Y, Shima K, et al. Lymphocytic reaction to colorectal cancer is associated with longer survival, independent of lymph node count, microsatellite instability, and CpG island methylator phenotype. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15(20):6412–20. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1438. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

