Sepsis-associated encephalopathy: Autophagy and miRNAs regulate microglial activation
- PMID: 38439741
- PMCID: PMC10912956
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.15964
Sepsis-associated encephalopathy: Autophagy and miRNAs regulate microglial activation
Abstract
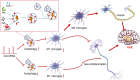
Sepsis-associated encephalopathy (SAE) describes diffuse or multifocal cerebral dysfunction caused by the systemic inflammatory response to sepsis. SAE is a common neurological complication in patients in the middle and late stages of sepsis in the intensive care unit. Microglia, resident macrophages of the central nervous system, phagocytose small numbers of neuronal cells and apoptotic cells, among other cells, to maintain the dynamic balance of the brain's internal environment. The neuroinflammatory response induced by activated microglia plays a central role in the pathogenesis of various central nervous system diseases. In this paper, we systematically describe the functions and phenotypes of microglia, summarize how microglia mediate neuroinflammation and contribute to the occurrence and development of SAE, and discuss recent progress in autophagy- and microRNA-mediated regulation of microglial activation to provide a theoretical basis for the prevention and treatment of SAE and identify related therapeutic targets.
Keywords: autophagy; microRNA; microglia; neuroinflammation; sepsis-associated encephalopathy.
© 2024 The Authors. Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Physiological Society and the American Physiological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Aloi, M. S. , Prater, K. E. , Sánchez, R. E. A. , Beck, A. , Pathan, J. L. , Davidson, S. , Wilson, A. , Keene, C. D. , de la Iglesia, H. , Jayadev, S. , & Garden, G. A. (2023). Microglia specific deletion of miR‐155 in Alzheimer's disease mouse models reduces amyloid‐β pathology but causes hyperexcitability and seizures. Journal of Neuroinflammation, 20, 60. 10.1186/s12974-023-02745-6 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beccari, S. , Sierra‐Torre, V. , Valero, J. , Pereira‐Iglesias, M. , García‐Zaballa, M. , Soria, F. N. , de Las Heras‐Garcia, L. , Carretero‐Guillen, A. , Capetillo‐Zarate, E. , Domercq, M. , Huguet, P. R. , Ramonet, D. , Osman, A. , Han, W. , Dominguez, C. , Faust, T. E. , Touzani, O. , Pampliega, O. , Boya, P. , … Sierra, A. (2023). Microglial phagocytosis dysfunction in stroke is driven by energy depletion and induction of autophagy. Autophagy, 1–30, 1952–1981. 10.1080/15548627.2023.2165313 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82060359;82360382/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- Qiankehe[2021]General088/Guizhou Province Social Development Project
- QiankeheFundamentalsZK[2022]Key049/Key Project of Guizhou Natural Science Foundation
- QiankehePlatformTalent[2021]No.5648/Guizhou Province Excellent Youth Science and Technology Talent Project
- ZunyouQingke(2020)No.2/Zunyi Excellent Youth Science and Technology Talent Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

