Melatonin alleviates oxidative stress damage in mouse testes induced by bisphenol A
- PMID: 38440074
- PMCID: PMC10910031
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1338828
Melatonin alleviates oxidative stress damage in mouse testes induced by bisphenol A
Abstract
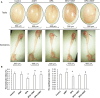
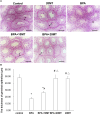
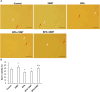
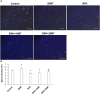
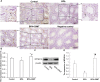
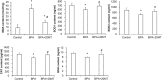
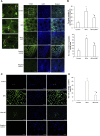
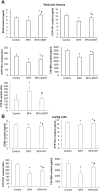
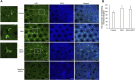
We investigated the effect of melatonin on bisphenol A (BPA)-induced oxidative stress damage in testicular tissue and Leydig cells. Mice were gavaged with 50 mg/kg BPA for 30 days, and concurrently, were injected with melatonin (10 mg/kg and 20 mg/kg). Leydig cells were treated with 10 μmol/L of BPA and melatonin. The morphology and organ index of the testis and epididymis were observed and calculated. The sperm viability and density were determined. The expressions of melatonin receptor 1A and luteinizing hormone receptor, and the levels of malonaldehyde, antioxidant enzymes, glutathione, steroid hormone synthases, aromatase, luteinizing hormone, testosterone, and estradiol were measured. TUNEL assay was utilized to detect testicular cell apoptosis. The administration of melatonin at 20 mg/kg significantly improved the testicular index and epididymis index in mice treated with BPA. Additionally, melatonin promoted the development of seminiferous tubules in the testes. Furthermore, the treatment with 20 mg/kg melatonin significantly increased sperm viability and sperm density in mice, while also promoting the expressions of melatonin receptor 1A and luteinizing hormone receptor in Leydig cells of BPA-treated mice. Significantly, melatonin reduced the level of malonaldehyde in testicular tissue and increased the expression of antioxidant enzymes (superoxide dismutase 1, superoxide dismutase 2, and catalase) as well as the content of glutathione. Moreover, melatonin also reduced the number of apoptotic Leydig cells and spermatogonia, aromatase expression, and estradiol level, while increasing the expression of steroid hormone synthases (steroidogenic acute regulatory protein, cytochrome P450 family 17a1, cytochrome P450 17α-hydroxylase/20-lyase, and, 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase) and the level of testosterone. Melatonin exhibited significant potential in alleviating testicular oxidative stress damage caused by BPA. These beneficial effects may be attributed to melatonin's ability to enhance the antioxidant capacity of testicular tissue, promote testosterone synthesis, and reduce testicular cell apoptosis.
Keywords: bisphenol A; melatonin; oxidative stress; testis; testosterone.
Copyright © 2024 Qi, Yang, Li, Liu, Xu, Wang, Feng and Pan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
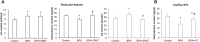
Similar articles
-
Melatonin Alleviates BPA-Induced Testicular Apoptosis and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2024 Mar 8;29(3):95. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2903095. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2024. PMID: 38538260
-
Melatonin controlled apoptosis and protected the testes and sperm quality against bisphenol A-induced oxidative toxicity.Toxicol Ind Health. 2016 Sep;32(9):1537-49. doi: 10.1177/0748233714561286. Epub 2014 Dec 23. Toxicol Ind Health. 2016. PMID: 25537623
-
Protective effects of exogenous melatonin therapy against oxidative stress to male reproductive tissue caused by anti-cancer chemical and radiation therapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of animal studies.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Aug 28;14:1184745. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1184745. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37701901 Free PMC article.
-
Efficiency of naringin against reproductive toxicity and testicular damages induced by bisphenol A in rats.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2019 Mar;22(3):315-523. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2019.29757.7184. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31156794 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of melatonin against the toxic effects of environmental pollutants and heavy metals on testicular tissue: A systematic review and meta-analysis of animal studies.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jan 30;14:1119553. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1119553. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36793277 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Protective Effects of Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome On Oxidative Stress-Induced Bisphenol-A in Isolated Rat Testes Mitochondria and Sperm Quality.JBRA Assist Reprod. 2025 Mar 12;29(1):53-60. doi: 10.5935/1518-0557.20240089. JBRA Assist Reprod. 2025. PMID: 39688440 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin as a potential adjuvant to mitigate depakine‑induced testicular damage in rats through its biological features.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2025 Jun 25;25(1):213. doi: 10.1186/s12906-025-04969-w. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2025. PMID: 40563113 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin Alleviates MBP-Induced Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in TM3 Cells via the SIRT1/PGC-1α Signaling Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 19;26(12):5910. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125910. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40565373 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akingbemi B. T., Sottas C. M., Koulova A. I., Klinefelter G. R., Hardy M. P. (2004). Inhibition of testicular steroidogenesis by the xenoestrogen bisphenol A is associated with reduced pituitary luteinizing hormone secretion and decreased steroidogenic enzyme gene expression in rat Leydig cells. Endocrinology 145 (2), 592–603. 10.1210/en.2003-1174 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Al-Griw M. A., Shalabi S. M., Alghazeer R. O., Elnfati A. H., Treesh S. A., Benjama A. E., et al. (2023). Nigella sativa oil alleviates mouse testis and sperm abnormalities induced by BPA potentially through redox homeostasis. Comb. Chem. High. Throughput Screen 26 (2), 301–312. 10.2174/1386207325666220514135606 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

