Christensenella minuta interacts with multiple gut bacteria
- PMID: 38440147
- PMCID: PMC10910051
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1301073
Christensenella minuta interacts with multiple gut bacteria
Abstract
Introduction: Gut microbes form complex networks that significantly influence host health and disease treatment. Interventions with the probiotic bacteria on the gut microbiota have been demonstrated to improve host well-being. As a representative of next-generation probiotics, Christensenella minuta (C. minuta) plays a critical role in regulating energy balance and metabolic homeostasis in human bodies, showing potential in treating metabolic disorders and reducing inflammation. However, interactions of C. minuta with the members of the networked gut microbiota have rarely been explored.
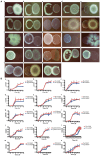
Methods: In this study, we investigated the impact of C. minuta on fecal microbiota via metagenomic sequencing, focusing on retrieving bacterial strains and coculture assays of C. minuta with associated microbial partners.
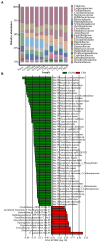
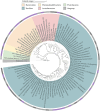
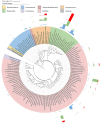
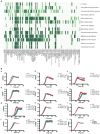
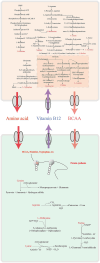
Results: Our results showed that C. minuta intervention significantly reduced the diversity of fecal microorganisms, but specifically enhanced some groups of bacteria, such as Lactobacillaceae. C. minuta selectively enriched bacterial pathways that compensated for its metabolic defects on vitamin B1, B12, serine, and glutamate synthesis. Meanwhile, C. minuta cross-feeds Faecalibacterium prausnitzii and other bacteria via the production of arginine, branched-chain amino acids, fumaric acids and short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), such as acetic. Both metagenomic data analysis and culture experiments revealed that C. minuta negatively correlated with Klebsiella pneumoniae and 14 other bacterial taxa, while positively correlated with F. prausnitzii. Our results advance our comprehension of C. minuta's in modulating the gut microbial network.
Conclusions: C. minuta disrupts the composition of the fecal microbiota. This disturbance is manifested through cross-feeding, nutritional competition, and supplementation of its own metabolic deficiencies, resulting in the specific enrichment or inhibition of the growth of certain bacteria. This study will shed light on the application of C. minuta as a probiotic for effective interventions on gut microbiomes and improvement of host health.
Keywords: Christensenellaceae; Faecalibacterium prausnitzii; Klebsiella pneumoniae; co-occurrence network; intestinal microorganism; nutrient cross-feeding.
Copyright © 2024 Xu, Jiang, Feng, Jiang, Wang and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The keystone gut species Christensenella minuta boosts gut microbial biomass and voluntary physical activity in mice.mBio. 2024 Feb 14;15(2):e0283623. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02836-23. Epub 2023 Dec 22. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38132571 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying a Novel Bile Salt Hydrolase from the Keystone Gut Bacterium Christensenella minuta.Microorganisms. 2021 Jun 9;9(6):1252. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9061252. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34207623 Free PMC article.
-
A Keystone Gut Bacterium Christensenella minuta-A Potential Biotherapeutic Agent for Obesity and Associated Metabolic Diseases.Foods. 2023 Jun 26;12(13):2485. doi: 10.3390/foods12132485. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37444223 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Species-targeted sorting and cultivation of commensal bacteria from the gut microbiome using flow cytometry under anaerobic conditions.Microbiome. 2022 Feb 3;10(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s40168-021-01206-7. Microbiome. 2022. PMID: 35115054 Free PMC article.
-
Christensenella minuta, a new candidate next-generation probiotic: current evidence and future trajectories.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jan 11;14:1241259. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1241259. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38274765 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gut microbiota in centenarians: A potential metabolic and aging regulator in the study of extreme longevity.Aging Med (Milton). 2024 Jun 14;7(3):406-413. doi: 10.1002/agm2.12336. eCollection 2024 Jun. Aging Med (Milton). 2024. PMID: 38975304 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oat Beta-Glucans Modulate the Gut Microbiome, Barrier Function, and Immune Responses in an In Vivo Model of Early-Stage Colorectal Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 19;25(24):13586. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413586. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39769349 Free PMC article.
-
The engineering of TBBPA-degrading synthetic microbiomes with integrated strategies.NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2025 Jul 19;11(1):139. doi: 10.1038/s41522-025-00777-9. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2025. PMID: 40683886 Free PMC article.
-
Christensenella minuta Alleviates Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity by Regulating Phenylalanine Metabolism.Nutrients. 2024 Jul 18;16(14):2314. doi: 10.3390/nu16142314. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39064757 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bai Z., Zhang N., Jin Y., Chen L., Mao Y., Sun L., et al. . (2022). Comprehensive analysis of 84 Faecalibacterium prausnitzii strains uncovers their genetic diversity, functional characteristics, and potential risks. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 12:919701. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.919701, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

