Comparative effects of incretin-based therapy on doxorubicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats: the role of SIRT1/Nrf2/NF-κB/TNF-α signaling pathways
- PMID: 38440177
- PMCID: PMC10910313
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1353029
Comparative effects of incretin-based therapy on doxorubicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats: the role of SIRT1/Nrf2/NF-κB/TNF-α signaling pathways
Abstract
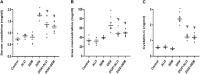
Introduction: Nephrotoxicity represents a major complication of using doxorubicin (DOX) in the management of several types of cancers. Increased oxidative stress and the activation of inflammatory mediators play outstanding roles in the development of DOX-induced kidney damage. This study aimed to investigate whether the two pathways of incretin-based therapy, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (presented as semaglutide, SEM) and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor (presented as alogliptin, ALO), differentially protect against DOX-induced nephrotoxicity in rats and to clarify the underlying molecular mechanisms. Methods: Adult male rats were divided into six groups: control (received the vehicle), DOX (20 mg/kg, single I.P. on day 8), DOX + ALO (20 mg/kg/day, P.O. for 10 days), DOX + SEM (12 μg/kg/day, S.C. for 10 days), ALO-alone, and SEM-alone groups. At the end of the study, the animals were sacrificed and their kidney functions, oxidative stress, and inflammatory markers were assessed. Kidney sections were also subjected to histopathological examinations. Results: The co-treatment with either ALO or SEM manifested an improvement in the kidney functions, as evidenced by lower serum concentrations of creatinine, urea, and cystatin C compared to the DOX group. Lower levels of MDA, higher levels of GSH, and increased SOD activity were observed in either ALO- or SEM-treated groups than those observed in the DOX group. DOX administration resulted in decreased renal expressions of sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) and Nrf2 with increased NF-κB and TNF-α expressions, and these effects were ameliorated by treatment with either ALO or SEM. Discussion: Co-treatment with either ALO or SEM showed a renoprotective effect that was mediated by their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects via the SIRT1/Nrf2/NF-κB/TNF-α pathway. The fact that both pathways of the incretin-based therapy demonstrate an equally positive effect in alleviating DOX-induced renal damage is equally noteworthy.
Keywords: dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor; doxorubicin; glucagon-like peptide-1; incretins; nephrotoxicity.
Copyright © 2024 Botros, Matouk, Amin and Heeba.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures








References
-
- Afsar T., Razak S., Almajwal A., Al-Disi D. (2020). Doxorubicin-induced alterations in kidney functioning, oxidative stress, DNA damage, and renal tissue morphology; Improvement by Acacia hydaspica tannin-rich ethyl acetate fraction. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. Sep. 27, 2251–2260. Epub 2020/09/05. 10.1016/j.sjbs.2020.07.011 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alghorabi A. A., Kabel A. M., Elmaaboud M. (2019). Doxorubicin: insights into dynamics, clinical uses and adverse effects. J. Cancer Res. Treat. 7, 17–20. 10.12691/jcrt-7-1-3 - DOI
-
- Al-Kuraishy H. M., Issa H. K., Al-Gareeb A. I., El-Bouseary M. M., Youssef A., Abdelaziz A. S., et al. (2022). The role of ivabradine in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: exploring of underlying argument. Inflammopharmacology. Dec 30, 2441–2446. Epub 2022/10/12. 10.1007/s10787-022-01082-z - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

