Exploring the chemical and pharmacological variability of Lepidium meyenii: a comprehensive review of the effects of maca
- PMID: 38440178
- PMCID: PMC10910417
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1360422
Exploring the chemical and pharmacological variability of Lepidium meyenii: a comprehensive review of the effects of maca
Abstract
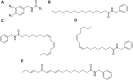
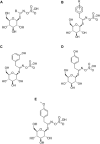
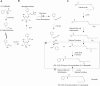
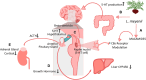
Maca (Lepidium meyenii), a biennial herbaceous plant indigenous to the Andes Mountains, has a rich history of traditional use for its purported health benefits. Maca's chemical composition varies due to ecotypes, growth conditions, and post-harvest processing, contributing to its intricate phytochemical profile, including, macamides, macaenes, and glucosinolates, among other components. This review provides an in-depth revision and analysis of Maca's diverse bioactive metabolites, focusing on the pharmacological properties registered in pre-clinical and clinical studies. Maca is generally safe, with rare adverse effects, supported by preclinical studies revealing low toxicity and good human tolerance. Preclinical investigations highlight the benefits attributed to Maca compounds, including neuroprotection, anti-inflammatory properties, immunoregulation, and antioxidant effects. Maca has also shown potential for enhancing fertility, combating fatigue, and exhibiting potential antitumor properties. Maca's versatility extends to metabolic regulation, gastrointestinal health, cardio protection, antihypertensive activity, photoprotection, muscle growth, hepatoprotection, proangiogenic effects, antithrombotic properties, and antiallergic activity. Clinical studies, primarily focused on sexual health, indicate improved sexual desire, erectile function, and subjective wellbeing in men. Maca also shows promise in alleviating menopausal symptoms in women and enhancing physical performance. Further research is essential to uncover the mechanisms and clinical applications of Maca's unique bioactive metabolites, solidifying its place as a subject of growing scientific interest.
Keywords: Lepidium meyenii; clinical studies; glucosilonates; maca; macaenes; macamides; pharmacology; preclinical.
Copyright © 2024 Ulloa del Carpio, Alvarado-Corella, Quiñones-Laveriano, Araya-Sibaja, Vega-Baudrit, Monagas-Juan, Navarro-Hoyos and Villar-López.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Is the hype around the reproductive health claims of maca (Lepidium meyenii Walp.) justified?J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Jan 30;211:126-170. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.08.003. Epub 2017 Aug 12. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28811221 Review.
-
[Research and application progress of Lepidium meyenii(maca)].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2018 Dec;43(23):4599-4607. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.2018.0122. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 30717548 Review. Chinese.
-
Not All Maca Is Created Equal: A Review of Colors, Nutrition, Phytochemicals, and Clinical Uses.Nutrients. 2024 Feb 14;16(4):530. doi: 10.3390/nu16040530. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38398854 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toxicological aspects of the South American herbs cat's claw (Uncaria tomentosa) and Maca (Lepidium meyenii) : a critical synopsis.Toxicol Rev. 2005;24(1):11-35. doi: 10.2165/00139709-200524010-00002. Toxicol Rev. 2005. PMID: 16042502 Review.
-
In silico profiling for secondary metabolites from Lepidium meyenii (maca) by the pharmacophore and ligand-shape-based joint approach.Chin Med. 2016 Sep 26;11:42. doi: 10.1186/s13020-016-0112-y. eCollection 2016. Chin Med. 2016. PMID: 27708692 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Optimization of Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Bioactive Compounds from Maca Leaves Using the Taguchi Method.Molecules. 2025 Apr 6;30(7):1635. doi: 10.3390/molecules30071635. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40286259 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Peruvian maca (Lepidium meyenii) Root Extract on In Vitro Cultured Porcine Fibroblasts and Adipocytes.Molecules. 2025 Feb 12;30(4):847. doi: 10.3390/molecules30040847. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40005158 Free PMC article.
-
Lepidium peruvianum as a Source of Compounds with Anticancer and Cosmetic Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 8;25(19):10816. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910816. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39409148 Free PMC article.
-
Partial Replacement of Cassava Starch With Peruvian Maca Flour in Mortadella: Innovation in Functional Meat Products With Clean-Label Potential.J Food Sci. 2025 Jun;90(6):e70314. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.70314. J Food Sci. 2025. PMID: 40476759 Free PMC article.
-
Global Research Status of Maca (Lepidium Meyenii Walp.): A Bibliometric Analysis of Hotspots, Bursts, and Trends.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 Mar 27;19:2329-2349. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S499849. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 40165997 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alvarado A. T., Navarro C., Pineda M., Villanueva L., Muñoz A. M., Bendezú M. R., et al. (2022). Activity of Lepidium meyenii Walp (purple maca) in immunosuppressed Oryctolagus cuniculus (albino rabbits). Pharmacia 69, 501–507. 10.3897/pharmacia.69.e80033 - DOI
-
- Antoine E., Chirila S., Teodorescu C. (2019). A patented blend consisting of a combination of vitex agnus-castus extract, lepidium meyenii (maca) extract and active folate, a nutritional supplement for improving fertility in women. Maedica 14, 274–279. 10.26574/maedica.2019.14.3.274 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

