Influencing Factors on Cardiovascular Health in China
- PMID: 38440341
- PMCID: PMC10908586
- DOI: 10.26599/1671-5411.2024.01.009
Influencing Factors on Cardiovascular Health in China
Abstract
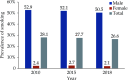
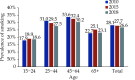
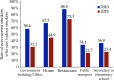
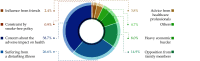
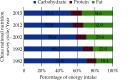
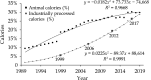
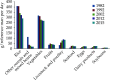
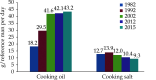
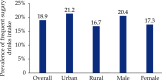
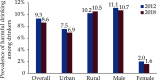
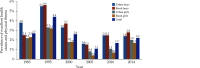
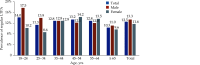
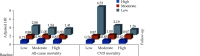
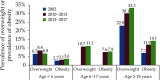
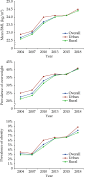
The Annual Report on Cardiovascular Health and Diseases in China (2022) intricate landscape of cardiovascular health in China. This is the first section of the report, which dissects influential factors across diverse domains. The investigation identifies tobacco use as a paramount concern, portraying China as the global epicenter of tobacco consumption. Cigarette smoking, exacerbated by second-hand smoke exposure, emerges as a critical and preventable risk factor, contributing to a surge in attributable deaths over the past three decades. In the realm of dietary nutrition, the study discerns an overall improvement, yet discerns worrisome deviations, notably an escalating fat intake surpassing recommended guidelines. The shifting dietary structure reveals diminished consumption of cereals and vegetables juxtaposed with an uptick in animal foods, while excessive intake of cooking oil and salt persists, straying substantially from endorsed levels. The exploration of physical activity patterns unfolds a nuanced narrative. Varied trends are observed among students, with concerns arising from sedentary behaviors and inadequate adherence to recommended guidelines. The analysis spans a trajectory of declining physical activity in Chinese adults, coupled with an alarming surge in sedentary leisure time, ultimately linking these factors to heightened risks of cardiovascular diseases and increased adiposity. An examination of overweight and obesity trends uncovers a relentless upward trajectory, projecting substantial prevalence by 2030. Noteworthy prevalence rates underscore the imperative for targeted interventions to curtail this burgeoning health crisis, with the anticipated prevalence extending to nearly two-thirds of the adult population. Psychological factors, notably depression, constitute an integral facet of cardiovascular health. Prevalence rates among patients with coronary artery disease and acute myocardial infarction underscore the intricate interplay between mental health and cardiovascular outcomes. Additionally, persistent depressive symptoms are shown to significantly elevate the risk of cardiovascular diseases and mortality. This first section underscores the multifaceted challenges facing cardiovascular health in China, emphasizing the imperative for tailored interventions across tobacco control, dietary habits, physical activity, obesity management, and psychological well-being to mitigate the escalating burden of cardiovascular diseases in the population.
© 2024 JGC All rights reserved; www.jgc301.com.
Figures
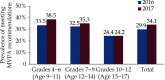
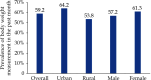
References
-
-
World Health Organization. WHO Report On The Global Tobacco Epidemic 2021: Addressing New And Emerging Products, 2021. WHO website. https://www.who.int/teams/health-promotion/tobacco-control/global-tobacco-report-2021.
-
-
-
Xiao L, Nan Y, Di XB, et al. [Study on the Current Status and Changing Trends of Smoking among People Aged 15 and Above in China 2018]. Zhong Hua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 2022; 43: 811–817. [Article in Chinese].
-
-
-
Zeng XY, Di XB, Liu SW, et al. 2021 Smoking behavior among secondary school students-China 2021. China CDC Wkly 2022; 4: 441–447.
-
-
-
2020 National Health Commission. China Smoking Hazardous to Health Report; People’s Medical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2021.
-
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
