Impact on Hearing Among SARS COV-2 Infected Adults and Children Born to Gestational COVID-19 Infected Mothers: A Prospective Case Control Study
- PMID: 38440441
- PMCID: PMC10908980
- DOI: 10.1007/s12070-023-04304-0
Impact on Hearing Among SARS COV-2 Infected Adults and Children Born to Gestational COVID-19 Infected Mothers: A Prospective Case Control Study
Abstract
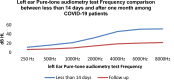
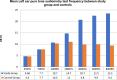
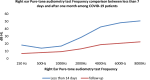
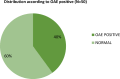
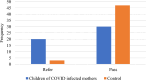
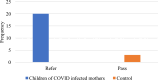
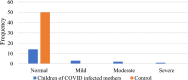
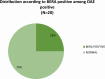
SARS COV 2 infection affects primarily the respiratory system and various organs in humans is responsible for higher mortality secondary to cytokine storm during the COVID-19 pandemic. It affects the internal auditory system is responsible for Sensory neural hearing loss in adults as well as children born to COVID-19 infected mothers. This study was aimed to detect the pattern of hearing loss in COVID-19 infected adults and pattern of hearing loss in children born to gestational COVID-19 infected mothers. Fifty asymptomatic RT-PCR COVID-19 infected adults and age, sex matched healthy controls were evaluated for audiological profile using Pure Tone Audiometry (PTA). Children born to COVID-19 infected mothers were tested using Transient product otoacoustic emissions and click-evoked auditory brainstem responses (ABRs) compared with children born to non-COVID mothers. PTA auditory profile of COVID-19 infected adults on day 7 had 30% (16 out of 50) significant high frequency sensory neural hearing impairment for 4000 Hz (p value 0.003), 6000 Hz (p value 0.001), 8000 Hz (p value 0.001). Repeat PTA testing on day 30 showed normal hearing. Whereas in children, 40% (n = 20) born to COVID-19 infected mothers had OAE as "Refer". BERA (ABRs) testing of that OAE "Refer" children revealed 30% (n = 6) hearing impairment. COVID-19 infection cause transient type of high frequency sensory neural hearing loss in adults. Whereas in children born to COVID-19 infected mothers there is risk of developing permanent, progressive or long-standing transient type of sensory neural hearing loss.
Keywords: Deafness; Gestational COVID-19; Hearing loss; SARS COVID-19.
© Association of Otolaryngologists of India 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Lechien JR, Chiesa-Estomba CM, De Siati DR. Olfactory and gustatory dysfunctions as a clinical presentation of mild-to-moderate forms of the coronavirus disease (COVID-19): a multicenter European study. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2020;277(8):2251–2261. doi: 10.1007/s00405-020-05965-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
