An Unusual Presentation of Angiolymphoid Hyperplasia with Eosinophilia as Postauricular Mass: A case Report
- PMID: 38440547
- PMCID: PMC10908713
- DOI: 10.1007/s12070-023-04178-2
An Unusual Presentation of Angiolymphoid Hyperplasia with Eosinophilia as Postauricular Mass: A case Report
Abstract
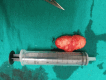
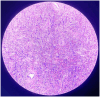
Angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia (ALHE) is a rare, benign, reactive vaso-proliferative condition in the dermal and subcutaneous tissues of the head and neck. A 28-year-old female presented with slow-growing painless swelling behind her left ear. FNAC revealed benign soft tissue neoplasm and histopathological examination after surgical excision revealed angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia. ALHE origin has been variously attributed to prior trauma, hyperestrogenemia, infectious agents, atopy, reactive hyperplasia, and benign neoplasia. Retroauricular ALHE has been rarely reported. However, on the basis of our case report, it should be a viable differential diagnosis when large subcutaneous tumors of the head and neck are encountered. When big subcutaneous tumors of the head and neck are present, especially in females, a valid differential diagnosis for angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia, a rare condition marked by dermal or subcutaneous endothelial cell proliferation, should also be considered.
Keywords: Angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia; Epithelioid hemangioma; Kimura Disease; Retroauricular.
© Association of Otolaryngologists of India 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of InterestNone.
Figures




References
-
- Onishi Y, Ohara K. Angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia associated with arteriovenous malformation: a clinicopathological correlation with angiography and serial estimation of serum levels of renin, eosinophil cationic protein and interleukin 5. Br J Dermatol. 1999;140(6):1153–1156. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2133.1999.02880.x. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
