Prognostic Role of Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio in Allergic Rhinitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- PMID: 38440632
- PMCID: PMC10909046
- DOI: 10.1007/s12070-023-04148-8
Prognostic Role of Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio in Allergic Rhinitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Abstract
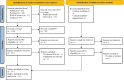
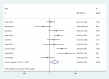
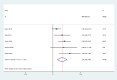
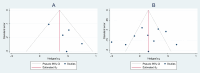
One of the crucial triggers of allergic diseases is an inflammatory reaction and neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) is one of the systemic inflammation biomarkers. Our review aimed to evaluate role of NLR in predicting severity and comorbidities of allergic rhinitis (AR). We systematically searched Scopus, Web of Science, and PubMed to find relevant studies. Standardized mean difference (SMD) with a 95% confidence interval (CI) was reported. Due to the high levels of heterogeneity, the random-effects model was used to generate pooled effects. Eleven articles were included in the systematic review, among which ten were included in meta-analysis including 1122 healthy controls and 1423 patients with AR. We found that patients with AR had a significantly higher level of NLR than healthy controls (SMD = 0.19, 95%CI = 0.03-0.36, P = 0.03). In addition, patients with moderate to severe AR had significantly higher levels of NLR compared to those with mild AR (SMD = 0.41, 95%CI = 0.20-0.63, P < 0.001). Interestingly, it was found that NLR could associate with some comorbidities of AR, like asthma. Our results confirmed that NLR could assist clinicians in predicting the severity and comorbidities of AR.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s12070-023-04148-8.
Keywords: Allergic rhinitis; Meta-analysis; NLR; Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio.
© Association of Otolaryngologists of India 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Is neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio associated with the severity of allergic rhinitis in children?Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016 Oct;273(10):3175-8. doi: 10.1007/s00405-015-3819-y. Epub 2015 Nov 2. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016. PMID: 26525883
-
The association between the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, and monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio and systemic sclerosis and its complications: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Immunol. 2024 May 10;15:1395993. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1395993. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38799443 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic significance of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in endometriosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Womens Health. 2023 Nov 7;23(1):576. doi: 10.1186/s12905-023-02692-7. BMC Womens Health. 2023. PMID: 37936116 Free PMC article.
-
Association of severity of allergic rhinitis with neutrophil-to-lymphocyte, eosinophil-to-neutrophil, and eosinophil-to-lymphocyte ratios in adults.Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2021 Sep 1;49(5):94-99. doi: 10.15586/aei.v49i5.204. eCollection 2021. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2021. PMID: 34476928
-
Prognostic Role of Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio in Contrast-Induced Nephropathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Angiology. 2024 Mar 15:33197241238512. doi: 10.1177/00033197241238512. Online ahead of print. Angiology. 2024. PMID: 38488664 Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic significance of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy: a meta-analysis.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Nov 27;29(1):562. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-02155-1. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39593107 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Value of Serum Cancer Antigen 125, Carcinoembryonic Antigen, Cancer Antigen 19-9, Anti Müllerian Hormone, White Blood Cell Count, Platelet Count, and Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio in Endometriosis: A Retrospective Study.Int J Fertil Steril. 2025 May 14;19(3):259-263. doi: 10.22074/ijfs.2024.2010957.1534. Int J Fertil Steril. 2025. PMID: 40590284 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dogru M, Citli R. The neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in children with atopic dermatitis: a case-control study. Clin Ter. 2017;168(4):e262–e265. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
