Anthelmintic and therapeutic effects of the biogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles against acute kidney injury induced by Parascaris equorum Infection in rats
- PMID: 38440749
- PMCID: PMC10908720
- DOI: 10.1007/s12639-023-01637-z
Anthelmintic and therapeutic effects of the biogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles against acute kidney injury induced by Parascaris equorum Infection in rats
Abstract
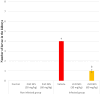
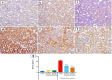
Complications of parasite infections, especially kidney disease, have been linked to poorer outcomes. Acute kidney damage, glomerulonephritis, and tubular dysfunction are the most prevalent renal consequences of Parascaris equorum infection. The purpose of this study was to determine the pharmacological effects of green-produced zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) on P. equorum infection in male Wistar rats. Thirty-six male rats were divided into two groups of 18 each: infected and non-infected. Both groups were separated into three subgroups, each of which received distilled water, 30 mg/kg ZnO NPs, and 60 mg/kg ZnO NPs. After 10 days of ZnO NPs administration, four larvae per gram of kidney tissue were present in the untreated infected group. While, no larvae were present in ZnO NPs (30 mg/kg) treated group, and one larva/g.tissue was present in ZnO NPs (60 mg/kg) treated group compared to untreated infected animals. P. equorum infected rats had increased kidney biomarkers (creatinine, urea, uric acid), malondialdehyde, and nitric oxide, with a significant decrease in their antioxidant systems. On the other hand, infected treated rats with green-produced zinc oxide nanoparticles had a substantial drop in creatinine, urea, uric acid, malondialdehyde, and nitric oxide, as well as a significant rise in their antioxidant systems. P. equorum infection in rats caused severe degenerative and necrotic renal tissues. On the other hand, there were no detectable histopathological alterations in rats treated with ZnO NPs (30, 60 mg/kg) as compared to the infected untreated animals. When compared to infected untreated mice, immunohistochemical examination of nuclear factor-kappa B showed a significant decrease during treatment with ZnO NPs (30, 60 mg/kg). Green-produced zinc oxide nanoparticles are a viable therapeutic strategy for Parascaris equorum infection due to their potent anthelmintic activity, including a significant decrease in larval burden in infected treated rats.
Keywords: Anthelmintic; Larvae; Nanoparticles; Parascaris equorum.
© Indian Society for Parasitology 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest regarding the content of this article. All the datasets generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Figures



References
-
- Alajmi RA, et al. Anti-toxoplasma activity of silver nanoparticles green synthesized with Phoenix dactylifera and Ziziphus spina-christi extracts which inhibits inflammation through liver regulation of cytokines in Balb/c mice. Biosci Rep. 2019;39(5):BSR20190379. doi: 10.1042/BSR20190379. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alhusseiny S, El-Beshbishi S. Nuclear factor-kappa B signaling pathways and parasitic Infections: an overview. Parasitol United J. 2021 doi: 10.21608/puj.2021.91389.1129. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
