Assessment of arterial pulsatility of cerebral perforating arteries using 7T high-resolution dual-VENC phase-contrast MRI
- PMID: 38440807
- PMCID: PMC11186522
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.30073
Assessment of arterial pulsatility of cerebral perforating arteries using 7T high-resolution dual-VENC phase-contrast MRI
Abstract
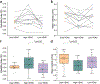
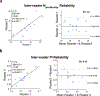
Purpose: Directly imaging the function of cerebral perforating arteries could provide valuable insight into the pathology of cerebral small vessel diseases (cSVD). Arterial pulsatility has been identified as a useful biomarker for assessing vascular dysfunction. In this study, we investigate the feasibility and reliability of using dual velocity encoding (VENC) phase-contrast MRI (PC-MRI) to measure the pulsatility of cerebral perforating arteries at 7 T.
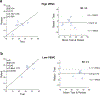
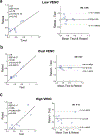
Methods: Twenty participants, including 12 young volunteers and 8 elder adults, underwent high-resolution 2D PC-MRI scans with VENCs of 20 cm/s and 40 cm/s at 7T. The sensitivity of perforator detection and the reliability of pulsatility measurement of cerebral perforating arteries using dual-VENC PC-MRI were evaluated by comparison with the single-VENC data. The effects of temporal resolution in the PC-MRI acquisition and aging on the pulsatility measurements were investigated.
Results: Compared to the single VENCs, dual-VENC PC-MRI provided improved sensitivity of perforator detection and more reliable pulsatility measurements. Temporal resolution impacted the pulsatility measurements, as decreasing temporal resolution led to an underestimation of pulsatility. Elderly adults had elevated pulsatility in cerebral perforating arteries compared to young adults, but there was no difference in the number of detected perforators between the two age groups.
Conclusion: Dual-VENC PC-MRI is a reliable imaging method for the assessment of pulsatility of cerebral perforating arteries, which could be useful as a potential imaging biomarker of aging and cSVD.
Keywords: arterial pulsatility; cerebral perforating artery; dual‐VENC; phase‐contrast MRI; pulsatility index (PI); ultra‐high field 7 T.
© 2024 The Authors. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Figures


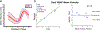
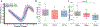

Similar articles
-
Simultaneous Assessment of Arterial Pulsatility Across Multiple Segments of Cerebral Arteries Using Multiband Dual-VENC Phase-Contrast MRI.NMR Biomed. 2025 Sep;38(9):e70099. doi: 10.1002/nbm.70099. NMR Biomed. 2025. PMID: 40660880 Free PMC article.
-
Blood Flow Velocity Analysis in Cerebral Perforating Arteries on 7T 2D Phase Contrast MRI with an Open-Source Software Tool (SELMA).Neuroinformatics. 2025 Jan 22;23(2):11. doi: 10.1007/s12021-024-09703-4. Neuroinformatics. 2025. PMID: 39841291 Free PMC article.
-
MarkVCID cerebral small vessel consortium: II. Neuroimaging protocols.Alzheimers Dement. 2021 Apr;17(4):716-725. doi: 10.1002/alz.12216. Epub 2021 Jan 21. Alzheimers Dement. 2021. PMID: 33480157 Free PMC article.
-
Antithrombotic therapy to prevent cognitive decline in people with small vessel disease on neuroimaging but without dementia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jul 14;7(7):CD012269. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012269.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35833913 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic resonance perfusion for differentiating low-grade from high-grade gliomas at first presentation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 22;1(1):CD011551. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011551.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29357120 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Simultaneous Assessment of Arterial Pulsatility Across Multiple Segments of Cerebral Arteries Using Multiband Dual-VENC Phase-Contrast MRI.NMR Biomed. 2025 Sep;38(9):e70099. doi: 10.1002/nbm.70099. NMR Biomed. 2025. PMID: 40660880 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing Cerebral Microvascular Volumetric Pulsatility with High-Resolution 4D CBV MRI at 7T.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 5:2024.09.04.24313077. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.04.24313077. medRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39281763 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Highlights of the society for magnetic resonance angiography 2024 conference.J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2025 Summer;27(1):101878. doi: 10.1016/j.jocmr.2025.101878. Epub 2025 Mar 12. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2025. PMID: 40086635 Free PMC article.
-
MVP-VSASL: measuring MicroVascular Pulsatility using velocity-selective arterial spin labeling.Magn Reson Med. 2025 Apr;93(4):1516-1534. doi: 10.1002/mrm.30370. Epub 2024 Dec 29. Magn Reson Med. 2025. PMID: 39888133 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous and synchronous characterization of blood and CSF flow dynamics using multiple Venc PC MRI.Imaging Neurosci (Camb). 2025 Mar 27;3:imag_a_00521. doi: 10.1162/imag_a_00521. eCollection 2025. Imaging Neurosci (Camb). 2025. PMID: 40800961 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pantoni L Cerebral small vessel disease: from pathogenesis and clinical characteristics to therapeutic challenges. Lancet Neurol 2010;9(7):689–701. - PubMed
-
- Pavlovic AM, Pekmezovic T, Tomic G, Trajkovic JZ, Sternic N. Baseline predictors of cognitive decline in patients with cerebral small vessel disease. J Alzheimers Dis 2014;42 Suppl 3:S37–43. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

