A global study on knowledge and perception of HPV and HPV vaccination among young obstetricians and gynecologists
- PMID: 38440968
- PMCID: PMC10920966
- DOI: 10.4274/tjod.galenos.2024.31369
A global study on knowledge and perception of HPV and HPV vaccination among young obstetricians and gynecologists
Abstract
Objective: Our goal is to improve the understanding of human papillomavirus (HPV) and its vaccination among obstetrics and gynecology trainees and young specialists worldwide.
Materials and methods: This cross-sectional study was conducted through an online survey consisting of 28 questions by the World Association of Trainees in Obstetrics and Gynecology between February and August 2023. The questionnaire collected demographic data of the study participants and assessed the respondents' knowledge and perception of HPV, HPV vaccines, and vaccine dosing schedule.
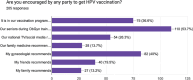
Results: Two hundred five Ob/Gyn trainees and young Ob/Gyns from 52 countries completed the survey. The majority of respondents were trainees (158, 77.1%). Most trainees and young Ob/Gyns learned about HPV for the first time during medical school (149, 72.6%). Almost all (204, 99.5%) Ob/Gyns responded that HPV was sexually transmitted. More than half of the respondents had not received HPV vaccination (110, 53.7%). The vaccine was recommended for respondents mostly by their Ob/Gyn senior colleagues (110, 53.7%). Most of the respondents knew how to manage HPV-positive patients (179, 87.3%).
Conclusion: This study suggests that even though knowledge on HPV and its vaccination is satisfactory among trainees and young Ob/Gyns, HPV vaccination remains deficient. There is a need to understand, educate, and address the potential problem that lies underneath.
Keywords: Human papillomavirus; gynecology; obstetrics; residency; vaccination.
Copyright© 2024 The Author. Published by Galenos Publishing House on behalf of Turkish Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: No conflict of interest was declared by the authors.
Figures
References
-
- Lizano M, Berumen J, García-Carrancá A. HPV-related carcinogenesis: basic concepts, viral types and variants. Arch Med Res. 2009;40:428–34. - PubMed
-
- Brianti P, De Flammineis E, Mercuri SR. Review of HPV-related diseases and cancers. New Microbiol. 2017;40:80–5. - PubMed
-
- Sowemimo OO, Ojo OO, Fasubaa OB. Cervical cancer screening and practice in low resource countries: Nigeria as a case study. Trop J Obstet Gynaecol. 2017;34:170–6.
-
- Stewart TS, Moodley J, Walter FM. Population risk factors for late-stage presentation of cervical cancer in sub-Saharan Africa. Cancer Epidemiol. 2018;53:81–92. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous