Integrated bacterial transcriptome and host metabolome analysis reveals insights into " Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus" population dynamics in the fruit pith of three citrus cultivars with different tolerance
- PMID: 38440971
- PMCID: PMC10986616
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.04052-23
Integrated bacterial transcriptome and host metabolome analysis reveals insights into " Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus" population dynamics in the fruit pith of three citrus cultivars with different tolerance
Abstract
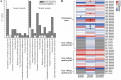
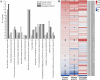
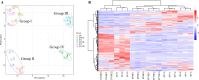
"Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus" (CLas), the causal agent of citrus Huanglongbing (HLB), is able to multiply to a high abundance in citrus fruit pith. However, little is known about the biological processes and phytochemical substances that are vital for CLas colonization and growth in fruit pith. In this study, CLas-infected fruit pith of three citrus cultivars ("Shatangju" mandarin, "Guanxi" pomelo, and "Shatian" pomelo) exhibiting different tolerance to CLas were collected and used for dual RNA-Seq and untargeted metabolome analysis. Comparative transcriptome analysis found that the activation of the CLas noncyclic TCA pathway and pathogenic-related effectors could contribute to the colonization and growth of CLas in fruit pith. The pre-established Type 2 prophage in the CLas genome and the induction of its CRISPR/cas system could enhance the phage resistance of CLas and, in turn, facilitate CLas population growth in fruit pith. CLas infection caused the accumulation of amino acids that were correlated with tolerance to CLas. The accumulation of most sugars and organic acids in CLas-infected fruit pith, which could be due to the phloem blockage caused by CLas infection, was thought to be beneficial for CLas growth in localized phloem tissue. The higher levels of flavonoids and terpenoids in the fruit pith of CLas-tolerant cultivars, particularly those known for their antimicrobial properties, could hinder the growth of CLas. This study advances our understanding of CLas multiplication in fruit pith and offers novel insight into metabolites that could be responsible for tolerance to CLas or essential to CLas population growth.IMPORTANCECitrus Huanglongbing (HLB, also called citrus greening disease) is a highly destructive disease currently threatening citrus production worldwide. HLB is caused by an unculturable bacterial pathogen, "Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus" (CLas). However, the mechanism of CLas colonization and growth in citrus hosts is poorly understood. In this study, we utilized the fruit pith tissue, which was able to maintain the CLas at a high abundance, as the materials for dual RNA-Seq and untargeted metabolome analysis, aiming to reveal the biological processes and phytochemical substances that are vital for CLas colonization and growth. We provided a genome-wide CLas transcriptome landscape in the fruit pith of three citrus cultivars with different tolerance and identified the important genes/pathways that contribute to CLas colonization and growth in the fruit pith. Metabolome profiling identified the key metabolites, which were mainly affected by CLas infection and influenced the population dynamic of CLas in fruit pith.
Keywords: bacterial transcriptome; dual RNA-Seq; fruit pith; metabolome; population dynamics; “Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus”.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
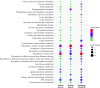

References
-
- Bové JM. 2006. Huanglongbing: a destructive, newly-emerging, century-old disease of citrus. J Plant Pathol:7–37. doi: 10.2307/41998278 - DOI
-
- Deng X, Tang W. 1996. The studies on detection of citrus Huanglongbing pathogen by polymerase chain reaction. J South China Agric Univ 17:119–120.
-
- Pan R, Chen Y, Deng X, Xu M. 2021. Digital gene expression analysis of Huanglongbing affected mandarins (Citrus reticulata Blanco) in response to thermotherapy. Hortic Plant J 7:1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2020.12.004 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

