Comparative transcriptional analysis of Candida auris biofilms following farnesol and tyrosol treatment
- PMID: 38440972
- PMCID: PMC10986546
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.02278-23
Comparative transcriptional analysis of Candida auris biofilms following farnesol and tyrosol treatment
Abstract
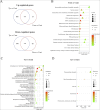
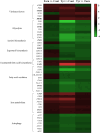
Candida auris is frequently associated with biofilm-related invasive infections. The resistant profile of these biofilms necessitates innovative therapeutic options, where quorum sensing may be a potential target. Farnesol and tyrosol are two fungal quorum-sensing molecules with antifungal effects at supraphysiological concentrations. Here, we performed genome-wide transcript profiling with C. auris biofilms following farnesol or tyrosol exposure using transcriptome sequencing (RNA-Seq). Since transition metals play a central role in fungal virulence and biofilm formation, levels of intracellular calcium, magnesium, and iron were determined following farnesol or tyrosol treatment using inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry. Farnesol caused an 89.9% and 73.8% significant reduction in the calcium and magnesium content, respectively, whereas tyrosol resulted in 82.6%, 76.6%, and 81.2% decrease in the calcium, magnesium, and iron content, respectively, compared to the control. Genes involved in biofilm events, glycolysis, ergosterol biosynthesis, fatty acid oxidation, iron metabolism, and autophagy were primarily affected in treated cells. To prove ergosterol quorum-sensing molecule interactions, microdilution-based susceptibility testing was performed, where the complexation of farnesol, but not tyrosol, with ergosterol was impeded in the presence of exogenous ergosterol, resulting in a minimum inhibitory concentration increase in the quorum-sensing molecules. This study revealed several farnesol- and tyrosol-specific responses, which will contribute to the development of alternative therapies against C. auris biofilms.
Importance: Candida auris is a multidrug-resistant fungal pathogen, which is frequently associated with biofilm-related infections. Candida-derived quorum-sensing molecules (farnesol and tyrosol) play a pivotal role in the regulation of fungal morphogenesis and biofilm development. Furthermore, they may have remarkable anti-biofilm effects, especially at supraphysiological concentrations. Innovative therapeutic approaches interfering with quorum sensing may be a promising future strategy against C. auris biofilms; however, limited data are currently available concerning farnesol-induced and tyrosol-related molecular effects in C. auris. Here, we detected several genes involved in biofilm events, glycolysis, ergosterol biosynthesis, fatty acid oxidation, iron metabolism, and autophagy, which were primarily influenced following farnesol or tyrosol exposure. Moreover, calcium, magnesium, and iron homeostasis were also significantly affected. These results reveal those molecular and physiological events, which may support the development of novel therapeutic approaches against C. auris biofilms.
Keywords: Candida auris; biofilm; calcium; ergosterol; iron; magnesium; quorum-sensing; transcriptome.
Conflict of interest statement
L.M. received conference travel grants from MSD, Cidara Therapeutics, Astellas, and Pfizer. All other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2019. Antibiotic resistance threats in the United States. Available from: https://ndc.services.cdc.gov/wp-content/uploads/Antibiotic-Resistance-Th...
-
- WHO fungal priority pathogens report. 2022. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240060241.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- NKFIH FK138462/Hungarian National Research, Development and Innovation Office
- BO/00127/21/8/Janos Bolyai Research Scholarship of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences
- UNKP-22-5-DE-417/New National Excellence Program of the Ministry for Innovation and Technology from the Source of the National Research, Development and Innovation Fund
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

