Cross Talks between CNS and CVS Diseases: An Alliance to Annihilate
- PMID: 38441007
- PMCID: PMC11284694
- DOI: 10.2174/011573403X278550240221112636
Cross Talks between CNS and CVS Diseases: An Alliance to Annihilate
Abstract
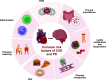
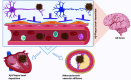
Cardiovascular and neurological diseases cause substantial morbidity and mortality globally. Moreover, cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death globally. About 17.9 million people are affected by cardiovascular diseases and 6.8 million people die every year due to neurological diseases. The common neurologic manifestations of cardiovascular illness include stroke syndrome which is responsible for unconsciousness and several other morbidities significantly diminished the quality of life of patients. Therefore, it is prudent need to explore the mechanistic and molecular connection between cardiovascular disorders and neurological disorders. The present review emphasizes the association between cardiovascular and neurological diseases specifically Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, and Huntington's disease.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Cardiovascular disorders; Huntington’s disease; Parkinson’s disease; neurological disorders; oxidative stress..
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.net.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Synopsis on the linkage of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease with chronic diseases.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2015 Jan;21(1):1-7. doi: 10.1111/cns.12344. Epub 2014 Nov 15. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2015. PMID: 25399848 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Global, regional, and national burden of neurological disorders during 1990-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015.Lancet Neurol. 2017 Nov;16(11):877-897. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(17)30299-5. Epub 2017 Sep 17. Lancet Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28931491 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebrovascular and Neurological Disorders: Protective Role of NRF2.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 12;20(14):3433. doi: 10.3390/ijms20143433. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31336872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Air Pollution and Central Nervous System Disease: A Review of the Impact of Fine Particulate Matter on Neurological Disorders.Front Public Health. 2020 Dec 16;8:575330. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2020.575330. eCollection 2020. Front Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33392129 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GABA-transaminase: A Key Player and Potential Therapeutic Target for Neurological Disorders.Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2024;24(1):57-67. doi: 10.2174/0118715249267700231116053516. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38243961 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

