GZ17-6.02 interacts with proteasome inhibitors to kill multiple myeloma cells
- PMID: 38441437
- PMCID: PMC10913917
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.28558
GZ17-6.02 interacts with proteasome inhibitors to kill multiple myeloma cells
Abstract
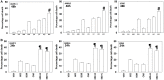
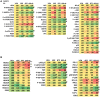
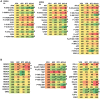
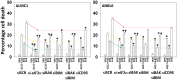
GZ17-6.02, a synthetically manufactured compound containing isovanillin, harmine and curcumin, has undergone phase I evaluation in patients with solid tumors (NCT03775525) with a recommended phase 2 dose (RP2D) of 375 mg PO BID. GZ17-6.02 was more efficacious as a single agent at killing multiple myeloma cells than had previously been observed in solid tumor cell types. GZ17-6.02 interacted with proteasome inhibitors in a greater than additive fashion to kill myeloma cells and alone it killed inhibitor-resistant cells to a similar extent. The drug combination of GZ17-6.02 and bortezomib activated ATM, the AMPK and PERK and inactivated ULK1, mTORC1, eIF2α, NFκB and the Hippo pathway. The combination increased ATG13 S318 phosphorylation and the expression of Beclin1, ATG5, BAK and BIM, and reduced the levels of BCL-XL and MCL1. GZ17-6.02 interacted with bortezomib to enhance autophagosome formation and autophagic flux, and knock down of ATM, AMPKα, ULK1, Beclin1 or ATG5 significantly reduced both autophagy and tumor cell killing. Knock down of BAK and BIM significantly reduced tumor cell killing. The expression of HDACs1/2/3 was significantly reduced beyond that previously observed in solid tumor cells and required autophagy. This was associated with increased acetylation and methylation of histone H3. Combined knock down of HDACs1/2/3 caused activation of ATM and the AMPK and caused inactivation of ULK1, mTORC1, NFκB and the Hippo pathway. HDAC knock down also enhanced ATG13 phosphorylation, increased BAK levels and reduced those of BCL-XL. Collectively, our present studies support performing additional in vivo studies with multiple myeloma cells.
Keywords: ER stress; GZ17-6.02; autophagy; bortezomib; proteasome inhibitor.
Conflict of interest statement
PD has received funding support from Genzada Pharmaceuticals Inc. for these studies. Dr. West is a paid officer of the company. Dr. Dent is a Consultant and Key Scientific advisor to the company. PD and CW thank Dr. Daniel Von Hoff, a consultant and key scientific advisor for Genzada Pharmaceuticals, for expert guidance during performance of these studies and for editing the manuscript.
Figures




Similar articles
-
GZ17-6.02 interacts with bexarotene to kill mycosis fungoides cells.Oncotarget. 2024 Feb 8;15:124-133. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.28557. Oncotarget. 2024. PMID: 38329728 Free PMC article.
-
GZ17-6.02 and axitinib interact to kill renal carcinoma cells.Oncotarget. 2022 Feb 4;13:281-290. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.28189. eCollection 2022. Oncotarget. 2022. PMID: 35136485 Free PMC article.
-
GZ17-6.02 and palbociclib interact to kill ER+ breast cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2022 Jan 11;13:92-104. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.28177. eCollection 2022. Oncotarget. 2022. PMID: 35035775 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of The Synergistic Effects of Curcumin with Proteasome Inhibitors in Multiple Myeloma Preclinical Models.Integr Cancer Ther. 2023 Jan-Dec;22:15347354231159322. doi: 10.1177/15347354231159322. Integr Cancer Ther. 2023. PMID: 36879488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms for synergistic effect of proteasome inhibitors with platinum-based therapy in solid tumors.Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2016 Feb;55(1):3-8. doi: 10.1016/j.tjog.2015.12.004. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2016. PMID: 26927239 Review.
References
-
- Albagoush SA, Shumway C, Azevedo AM. Multiple Myeloma. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024. - PubMed
-
- Leng Y, Hu X, Li L, Nkwocha J, Satta T, Sharma K, Kmeiciak M, Zhou H, Zhang Z, Zhou L, Chen W, Grant S. Mechanisms underlying synergism between circularized tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand and bortezomib in bortezomib-sensitive or -resistant myeloma cells. Hematol Oncol. 2022; 40:999–1008. 10.1002/hon.3045. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

