The impact of Lactococcus lactis KUST48 on the transcription profile of Aeromonas hydrophila-infected zebrafish spleen
- PMID: 38441470
- PMCID: PMC10986548
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.03927-23
The impact of Lactococcus lactis KUST48 on the transcription profile of Aeromonas hydrophila-infected zebrafish spleen
Abstract
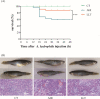
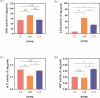
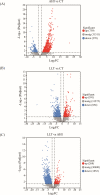
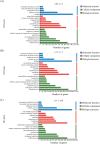
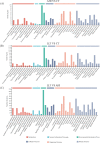
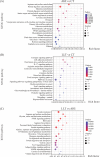
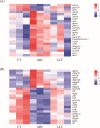
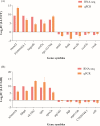
Aeromonas hydrophila, an aquatic pathogenic bacterium, has been found to infect many fish species and cause huge aquaculture losses. Antibiotics are the most common drugs used to treat these infections. However, antibiotic abuse can lead to the development of antibiotic resistance. Probiotics have the potential to replace antibiotics for preventing infections. Zebrafish (Danio rerio) is a model organism used to study the innate immune system and host-pathogen interactions. Currently, there is little information on how the fish immune system responds to A. hydrophila and probiotic treatment. To increase the understanding of the molecular mechanisms behind the zebrafish defense against A. hydrophila and provide evidence that antibiotics can be replaced by probiotics, a transcriptome analysis of the zebrafish spleen was conducted 48 hours after infection by A. hydrophila, as well as after treatment using Lactococcus lactis KUST48 4 hours after infection. A total of 36,499 genes were obtained. There were 3,337 genes found to have significant differential expression between treatment and control groups. According to further annotation and enrichment analysis, differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were involved in signal transduction, endocrine system cancer, and the immune system. Insulin resistance disappeared in the zebrafish after treatment. Quantitative real-time PCR was performed to confirm the significant regulation of immune defense DEGs, the results of which were consistent with the RNA-sequencing data. These results could serve as a basis for future studies on the immune response to A. hydrophila and provide suggestions for probiotic alternatives to antibiotics, which will be of great significance to aquaculture and environmental protection.IMPORTANCEIn recent years, the unreasonable use of antibiotics has led to the emergence of drug-resistant pathogenic bacteria, antibiotic residues, cross infection, toxic side effects, and so on, which has caused a serious threat to human food safety and life health. In recent years, many studies have demonstrated the potential of probiotics as a substitute for antibiotics, but there is still a lack of understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying probiotic therapy. We conduct a research on the impact of Lactococcus lactis KUST48 on the transcription profile of Aeromonas hydrophila-infected zebrafish spleen. Mortality of zebrafish infected with A. hydrophila was significantly reduced after treatment with L. lactis KUST48. Our results can help to strengthen our understanding of the pathogenic mechanisms of zebrafish and provide a valuable reference for the molecular mechanisms of probiotic therapy.
Keywords: Aeromonas hydrophila; Lactococcus lactis; immune response; transcriptome; zebrafish.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of Aeromonas hydrophila-induced intestinal inflammation and mucosal barrier function damage in crucian carp by oral administration of Lactococcus lactis.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018 Dec;83:359-367. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2018.09.041. Epub 2018 Sep 17. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30236608
-
Lactococcus lactis' Effect on the Intestinal Microbiota of Streptococcus agalactiae-Infected Zebrafish (Danio rerio).Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Oct 26;10(5):e0112822. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01128-22. Epub 2022 Oct 10. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36214699 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Lactococcus lactis from Cyprinus carpio L. as probiotics on growth performance, innate immune response and disease resistance against Aeromonas hydrophila.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019 Oct;93:73-81. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2019.07.028. Epub 2019 Jul 11. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31302283
-
Current prospects and challenges in fish vaccine development in India with special reference to Aeromonas hydrophila vaccine.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020 May;100:283-299. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2020.01.064. Epub 2020 Feb 20. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32088285 Review.
-
Aeromonas dhakensis: A Zoonotic Bacterium of Increasing Importance in Aquaculture.Pathogens. 2024 May 31;13(6):465. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13060465. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 38921763 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yu H, Zhang L, Feng C, Chi T, Qi Y, Abbas Raza SH, Gao N, Jia K, Zhang Y, Fan R, Cai R, Qian A, Li Y, Sun W, Shan X, Liu N, Zhang L. 2022. A phage cocktail in controlling phage resistance development in multidrug resistant Aeromonas hydrophila with great therapeutic potential. Microb Pathog 162:105374. doi:10.1016/j.micpath.2021.105374 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sun B-Y, He W, Yang H-X, Tian D-Y, Jian P-Y, Wu K, Yang C-G, Song X-H. 2022. Increased susceptibility to Aeromonas hydrophila infection in grass carp with antibiotic-induced intestinal dysbiosis. Aquaculture 552:737969. doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2022.737969 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

